Brain Abnormalities

It has been shown that exposure to EMFs increases behavior problems, ADHD, neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and ALS, depression, suicide, electromagnetic hypersensitivity, biological clock disturbance, and neurotransmitter dysfunction.
In recent years, academic performance is on the decline, and developmental disorders such as ADHD and autism, neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and ALS and multiple sclerosis, and depression and suicide are on the rise.
Some of these abnormalities began to increase around the time commercial cell phone service began, and EMFs are likely to be the major factor in their increase.
Recent Trends
Academic Performance :
Mathematics
Science
Reading
Average
Autism :
US
Developmental Disorders :
US
Japan
Dementia :
US
Finland
Alzheimer's :
US
Japan
Sweden
ALS :
Sweden
Japan
Multiple Sclerosis :
US
Europe
Japan
Depression :
US
Japan
Neurosis/Mood Disorders :
Japan
Suicide :
US
Table of ContentsAll_Pages
Behavior Problems and ADHD
First, I will present studies showing that behavior problems and ADHD increased and memory declined in children and adolescents with exposure to EMFs from cell phones, cell towers, Wi-Fi, and other sources.
I will also present studies showing that behavior problems in children increased with exposure of pregnant women to EMFs from cell phones.
These are likely to be due to some adverse effects of EMFs on the brains of fetuses, children, and adolescents.
In fact, animal experiments described below show that exposure to EMFs from cell phones and other sources damaged brains and decreased the number of brain cells in fetuses and pups of rats and mice.
Studies
Thomas et al. 2009
For children aged 8-12 years and adolescents aged 13-17 years in four cities in Bavaria, Germany, conduct problems increased as the strength of RF-EMFs they were exposed to during the day increased, emitted from cell phones, cell towers, and Wi-Fi.
Increase in Conduct Problems
In addition, hyperactivity in adolescents increased as the strength of RF-EMFs increased.
Increase in Hyperactivity
The odds of hyperactivity in adolescents increased 2-fold in the top 25% for the strength of RF-EMFs from cell phones, cell towers, and Wi-Fi.
Divan et al. 2008
For pregnant study participants recruited throughout Denmark, behavior problems increased in their children at age 7 when they had used their cell phones pre-birth or post-birth, especially pre-birth.
Increase in Behavior Problems
Guxens et al. 2013
For pregnant women in Amsterdam, Netherlands, behavior problems increased in their children at age 5 when they had used their cell phones during pregnancy.
Increase in Behavior Problem
Behavior problems in children at age 5 increased 2-fold with the use of cell phones during pregnancy.
Byun et al. 2013
For 3rd and 5th graders in 27 elementary schools in South Korea, ADHD increased when they used the Internet on their cell phones and as game time and call time on their cell phones increased.
Increase in ADHD with Internet
Increase in ADHD with Game
Increase in ADHD with Call
Other observations included a higher increase in ADHD when limited to children with higher blood lead levels.
Ghadamgahi et al. 2016
For students aged 10-12 years in four elementary schools in Tehran, Iran, Working Memory Index of the Wechsler Intelligence Test for Children declined when they attended schools located near a substation.
Decline in Memory
Working Memory Index declined by 10% when the elementary schoolers attended the schools near the substation.
Neurodegenerative Diseases
Next, I will present studies showing that neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and ALS increased with exposure to EMFs, mainly in the elderly.
I will also present a study showing that multiple sclerosis in women increased with exposure to EMFs from cell phones.
Studies
Feychting et al. 1998
For adults aged 50 or older on the Swedish twin registry, dementia and Alzheimer's desease increased as the strength of ELF-EMFs at workplaces increased.
This was especially more pronounced among relatively younger ones, aged 75 years or younger.
Increase in Dementia
The odds of dementia increased 4-fold with more than 0.2 μT of the ELF-EMFs at the workplaces and 6-fold for those aged 75 years or younger.
Increase in Alzheimer's Disease
The odds of Alzheimer's desease increased 3-fold with more than 0.2 μT of the ELF-EMFs at the workplaces and 5-fold for those aged 75 years or younger.
Sobel et al. 1995
For patients at the University of Southern California, the University of Helsinki, and Koskela Hospital in Helsinki, Alzheimer's desease increased when ELF-EMFs at workplaces were stronger.
This was especially more pronounced among women.
Increase in Alzheimer's Disease
The odds of Alzheimer's disease increased 3-fold with 0.2 μT or more of the ELF-EMFs at the workplaces, and 4-fold among the women.
Håkansson et al. 2003
For workers in the Swedish engineering industry, deaths from Alzheimer's disease and ALS increased as the strength of ELF-EMFs at workplaces increased.
Increase in Alzheimer's Disease
The mortality risk of Alzheimer's disease increased 4-fold with more than 0.53 μT of the ELF-EMFs at the workplaces.
Increase in ALS
The mortality risk of Alzheimer's disease increased 2-fold with more than 0.53 μT of the ELF-EMFs at the workplaces.
Luna et al. 2019
For residents in the Limousin region, France, ALS increased as the strength of RF-EMFs from cell towers increased.
Increase in ALS
The risk of ALS increased by 80% with more than 0.105 μW/cm2 of the RF-EMFs from the cell towers.
It is calculated from the strength of the electric field described in the paper, as the impedance of free space 377 Ω.
Harbo Poulsen et al. 2012
For women aged 18-64 throughout Denmark, the onset of multiple sclerosis and deaths increased when they used their cell phones for prolonged periods of time.
Increase in Multiple Sclerosis
Furthermore, the degree of increase for multiple sclerosis became greater when looking at the year in which the symptoms first appeared, rather than the year in which the patients were diagnosed by doctors.
Increase in Multiple Sclerosis
The incidence rate of multiple sclerosis increased 7-fold with 10 years or more of cell phone use.
Damage to the Brain
Next, I will present studies showing that exposure to EMFs from cell phones and other sources damaged a variety of parts in the brains of rats and mice.
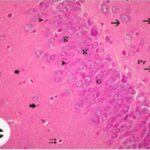
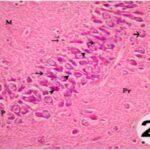
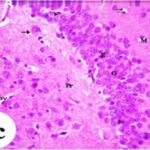
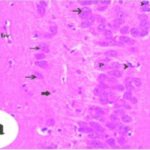
Dark Neurons
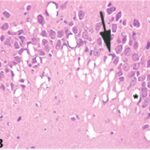
When brain tissue is damaged, there appear contracted, intensely stained neurons called dark neurons. Dark neurons are regarded as dying or degenerating neurons. (JORTNER 2006)
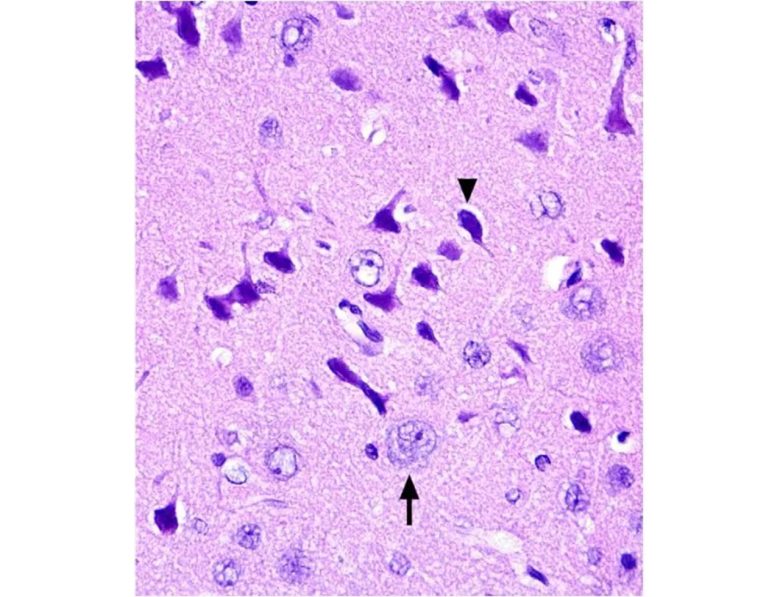
Dark Neurons (arrowhead) and Normal Neurons (arrow)
(Cited from JORTNER 2006)
Many studies have shown that dark neurons also appear in the brains of mice and rats exposed to EMFs, suggesting that EMFs damage the brain.
Damage to the Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a part of the brain involved in memory and learning and contains two main regions called the Ammon's horn and the dentate gyrus.
The major cells of the dentate gyrus and Ammon's horn are granule cells and pyramidal cells, respectively.
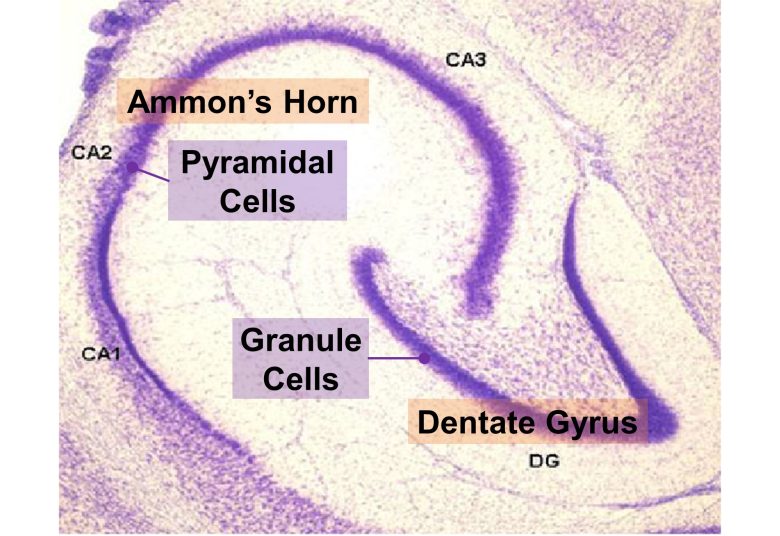
Structure of the Hippocampus
( Cited and modified from Nilufer Yonguc et al. 2012 )
It has been shown that the pathology of Alzheimer's disease begins with hippocampal atrophy, that the volume of the hippocampus is reduced in children with ADHD, and that the hippocampus is also atrophied in depression. (Dhikav and Anand 2011, Hoogman et al. 2017, Videbech 2004)
Also in diseases with hippocampal atrophy, declines in memory is observed. (Deweer et al. 1995, Isaacs et al. 2000, Aanes et al. 2019, Sheline et al. 1999)
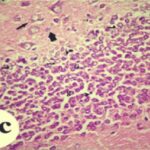
And, it has been shown that exposure to EMFs damages the hippocampus in rats, decreasing the number of granule and pyramidal cells.
Damage to Purkinje Cells
The cerebellar cortex is a part of the brain involved in controlling and learning movement, etc. It is composed of three layers: the molecular layer, the Purkinje cell layer, and the granule cell layer.
Among these, Purkinje cells are responsible for the primary output of the cerebellar cortex.
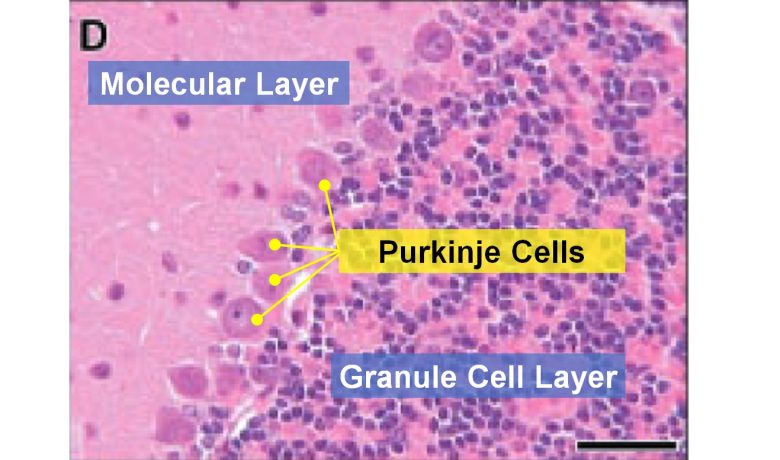
Structure of the Cerebellar Cortex
( Cited from Gupta et al. 2001 )
Marked Purkinje cell loss is the most consistent finding in the autistic disorder. (Kinnear Kern 2003)
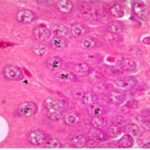
And, it has been shown that exposure to EMFs degenerates Purkinje cells in the cerebellar cortex of rats, decreasing their number.
Damage to Myelin Sheaths
Neurons are surrounded by sheath-like lipid layers called myelin sheaths. Myelin sheaths play a role in increasing the rate of neurotransmission.
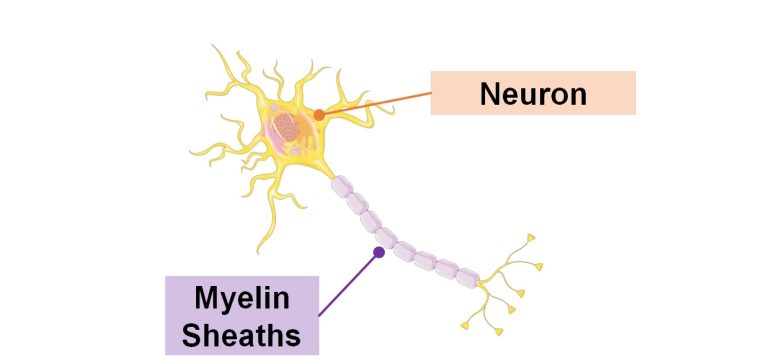
Damage to these myelin sheaths can lead to demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
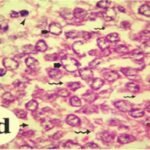
And, it has been shown that exposure to EMFs damages the myelin sheaths of rats and mice.
Studies
Salford et al. 2003
Rats aged 12-26 weeks, equivalent to adolescents/adults, were exposed to cell phone EMFs at a whole-body average SAR of 0.002-0.2 W/kg for only 2 hours.
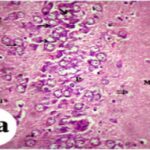
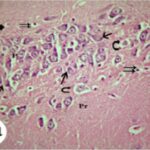
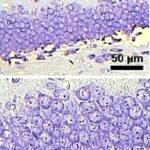
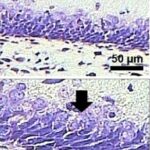
As a result, in the brains of the rats, the blood-brain barrier leaked, and dark neurons increased in the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and basal ganglia.
Leakage of the Blood-Brain Barrier
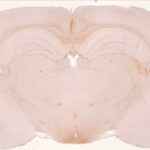
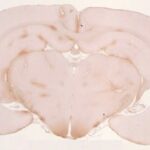
Due to the exposure to the cell phone EMFs, the blood-brain barrier was breached, and albumin leaked out.
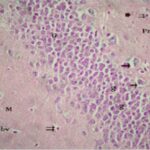
Increase in Dark Neurons 1
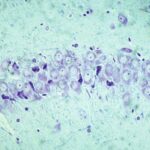
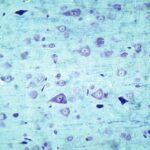
Due to the exposure to the cell phone EMFs, dark neurons increased in the cerebral cortex and hippocampal dentate gyrus.
Increase in Dark Neurons 2
The larger the whole-body average SAR, the more the dark neurons.
Odaci et al. 2008
Pregnant rats were exposed to 900 MHz RF-EMFs at a local SAR of 2 W/kg for 1 hour per day for 3 weeks during the entire pregnancy.
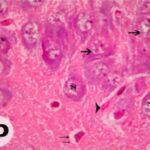
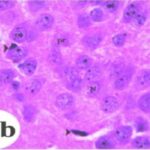
As a result, in the brains of the born-pup rats, granule cells in the hippocampal dentate gyrus became dark neurons, and the number of granule cells decreased.
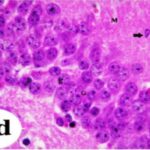
Increase in Dark Neurons
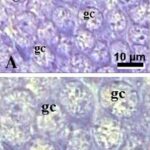
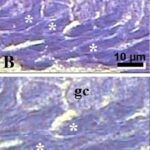
Due to the exposure to the RF-EMFs during pregnancy, a large number of shrunken, darkly stained granule cells, which seem to be dark neurons, appeared in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of the pup rats.
Decrease in Brain Cells
The number of granule cells in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of pup rats decreased by 20% due to the exposure to the RF-EMFs during pregnancy.
Bas et al. 2009
Pregnant rats were exposed to 900 MHz RF-EMFs at a local SAR of 2 W/kg for 1 hour per day for 3 weeks during the entire pregnancy.
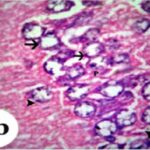
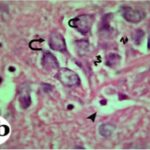
As a result, in the brains of the born-pup rats, pyramidal cells in the hippocampal Ammon's horn became dark neurons, and the number of pyramidal cells decreased.
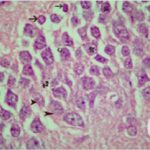
Increase in Dark Neurons
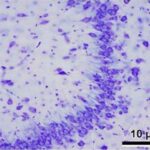
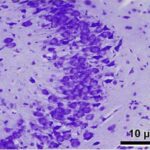
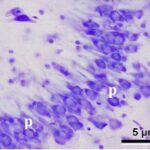
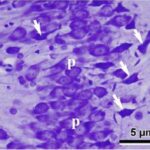
Due to the exposure to the RF-EMFs during pregnancy, a large number of shrunken, darkly stained pyramidal cells, which seem to be dark neurons, appeared in the hippocampal Ammon's horn of the pup rats.
Decrease in Brain Cells
The number of pyramidal cells in the hippocampal Ammon's horn of the pup rats decreased by 20% due to the exposure to the Rf-EMFs during pregnancy.
Akakin et al. 2020
Cell phones with a local SAR of 1.79 W/kg were placed on top of the breeding cages and kept on talk mode for 2 hours per day, and pregnant rats were exposed to their EMFs for a week in early pregnancy, and then the born-pup rats were exposed for another 2 months (equivalent to infancy/childhood).
As a result, in the brains of the pup rats, the cerebral cortex, hippocampal dentate gyrus, and hippocampal Ammon's horn were damaged, as well as the trigeminal nerves and their myelin sheaths.
Damage to the Brain
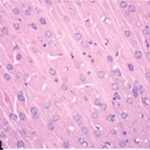
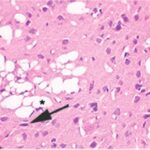
Due to the exposure to the cell phone EMFs during the fetushood, infancy, and childhood, numerous vacuoles (cavities) occurred in the cerebral cortex, and a large number of shrunken, darkly stained neurons, which seem to be dark neurons, appeared.
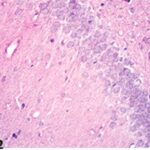
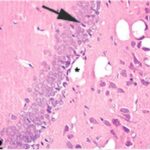
Due to the exposure to the cell phone EMFs during the fetushood, infancy, and childhood, numerous vacuoles (cavities) occurred in the hippocampal dentate gyrus, and a large number of shrunken, darkly stained neurons, which seem to be dark neurons, appeared.
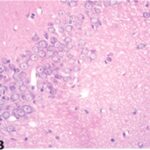
Due to the exposure to the cell phone EMFs during the fetushood, infancy, and childhood, numerous vacuoles (cavities) occurred in the hippocampal Ammon's horn, and a large number of shrunken, darkly stained neurons, which seem to be dark neurons, appeared.
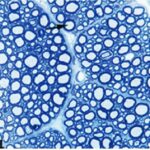
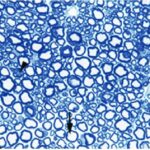
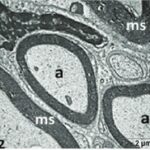
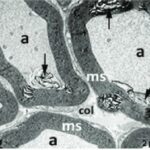
Due to the exposure to the cell phone EMFs during the fetushood, infancy, and childhood, the axons of the trigeminal nerves and their myelin sheaths were damaged.
Kim et al. 2017
Mice aged 6 weeks, equivalent to children/adolescents, were exposed to 835 MHz RF-EMFs at a local SAR of 4 W/kg for 5 hours per day for 12 weeks.
As a result, in the brains of the mice, myelin sheaths in the cerebral cortex were damaged.
An increase in hyperactivity was also observed, which is described in the section on Increase in Hyperactivity.
Damage to Myelin Sheaths
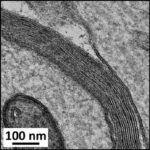
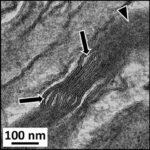
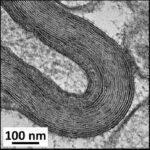
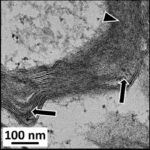
Due to the exposure to the RF-EMFs, myelin sheaths in the cerebral cortex were damaged.
Sonmez et al. 2010
Female rats aged 16 weeks, equivalent to an adolescent, were exposed to 900 MHz RF-EMFs at a local SAR of 2 W/kg for 1 hour per day for 4 weeks.
As a result, in the brains of the rats, the number of Purkinje cells in the cerebellar cortex decreased.
Decrease in Brain Cells 1
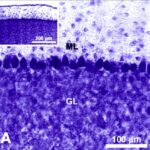
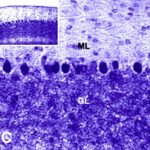
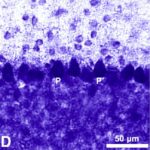
Due to the exposure to the RF-EMFs, the number of Purkinje cells in the cerebellar cortex decreased.
Decrease in Brain Cells 2
The number of Purkinje cells in the cerebellar cortex decreased by 10% due to the exposure to the RF-EMFs.
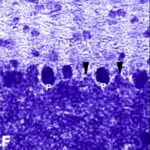
Ali et al. 2020
Second-generation (2G), third-generation (3G), and fourth-generation (4G) smartphones were placed on shelves in breeding cages and kept on data transmission for 1 hour per day, and rats aged 3-4 months, equivalent to adolescents, were exposed to their EMFs for 2 months.
As a result, in the brains of the rats, Purkinje cells in the cerebellar cortex became dark neurons as the communication protocols of smartphones became newer. (*)
However, since communication data differs between 2G for Internet communications, 3G for voice calls, and 4G for video calls, a simple comparison cannot be made.
Local SAR was 0.603 W/kg for 2G phones, unknown for 3G phones, and 0.628 W/kg for 4G phones.
Increase in Dark Neurons
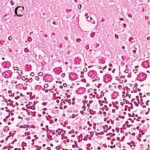
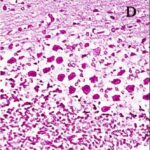
Due to the exposure to the smartphone EMFs, a large number of shrunken, darkly stained Purkinje cells, which seem to be dark neurons, appeared in the cerebellar cortex.
Megha et al. 2015
Male rats were exposed to RF-EMFs of 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 2450 MHz at whole-body average SARs of 0.00059 W/kg, 0.00058 W/kg, and 0.00066 W/kg, respectively, for 2 hours per day for 60 days.
As a result, in the hippocampi of the rats, reactive oxygen species (ROS) increased and inflammatory responses increased and DNA breaks increased as the frequency of the RF-EMFs increased.
Increase in ROS
An increase in lipid peroxidation and a decrease in antioxidant activity mean an increase in ROS.
The increase in inflammatory responses was indicated by an increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines, which have the ability to promote inflammatory responses.
Increase in Inflammatory Responses
The comet assay is used to detect DNA breaks. In the comet assay, the more the DNA breaks, the more the tail DNA, the longer the tail length, and the larger the olive tail moment.
Increase in DNA Breaks
Consequences of Damaged Brain
We have seen that exposure to EMFs from cell phones and other sources can damage the various parts of the brain of rats and mice.
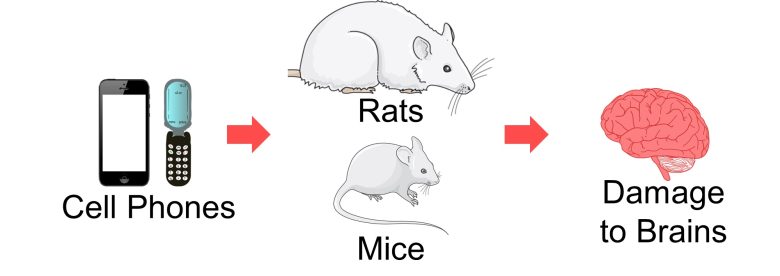
The damaged parts included the hippocampus, Purkinje cells in the cerebellar cortex, and myelin sheaths.
The following diseases associated with these damaged parts were mentioned at the beginning of this section.
Hippocampus
Alzheimer's disease, ADHD, depression, a decline in memory
Purkinje cells in the cerebellar cortex
Autism
Myelin sheaths
Demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis
With the exception of autism, these are all diseases for which increased risks in humans have been shown with EMF exposure.
Therefore, the animal experiments that we have just seen provide some support for the findings in humans.
As for the autism, the following recommendation have been made:
DNA damage, immune and blood–brain barrier disruption, cellular and oxidative stress, calcium channel, disturbed circadian rhythms, hormone dysregulation, and degraded cognition, sleep, autonomic regulation and brainwave activity all have commonalities between autism spectrum conditions and EMF, and the disruption of fertility and reproduction associated with EMF may also be related to the increasing incidence of autism spectrum conditions.
With dramatic increases in reported autism spectrum conditions that are coincident in time with the deployment of wireless technologies, we need aggressive investigation of potential autism spectrum conditions – EMF links.
However, no epidemiology examining such links seems to exist at this time.
Decline in Memory
Next, I will present studies showing that exposure to EMFs from cell phones and other sources declined memory in rats and mice.
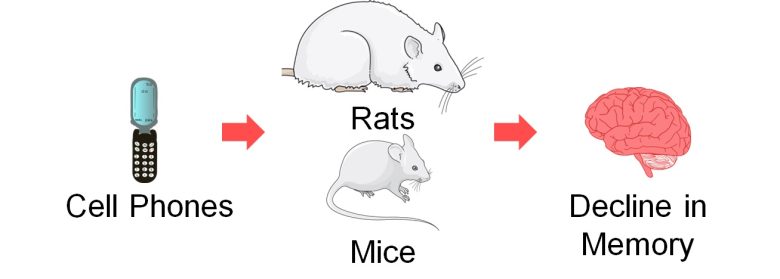
Studies
İkinci et al. 2013
Pregnant rats were exposed to 900 MHz RF-EMFs for 1 hour per day for 1 week in late pregnancy.
Next, the born-daughter rats were tested using the radial arm maze test and the passive avoidance test.
As a result, the rats showed a decline in their memory.
Radial Arm Maze Test
The radial arm maze test is a test that evaluates spatial learning and memory.
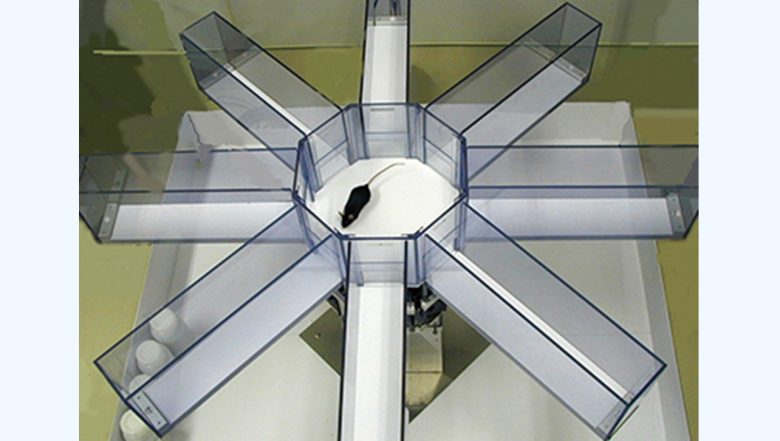
Food is placed at the tips of the device's eight arms, and a hungry rat goes around taking the food.
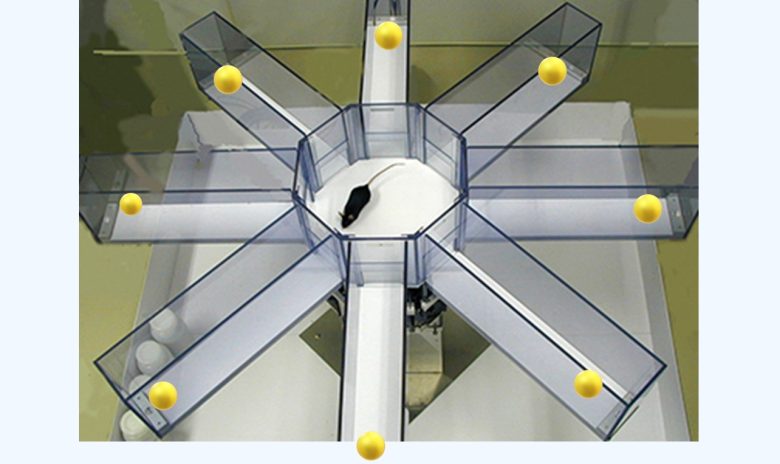
To feed efficiently, she needs to memorize the arms she has already visited and avoid going there.
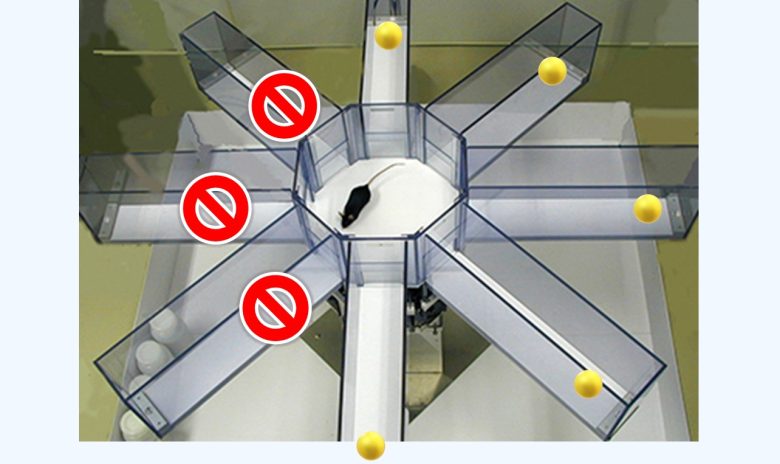
Her memory is evaluated by the time taken to select the correct arm (with food) and the number of wrong arm selections (without food).
Decline in Memory
Passive Avoidance Test
First, as a training phase, a rat is placed in a box divided into a dark room and a light room.
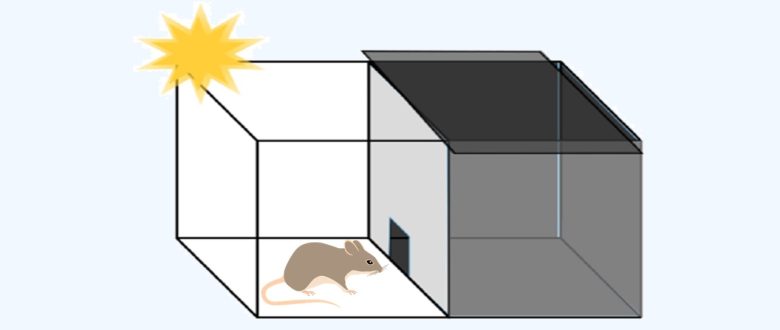
The rat will go into dark rooms since she likes the dark.
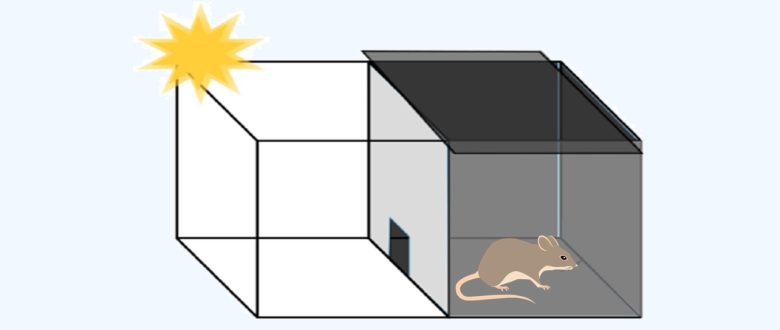
However, once entering the dark room, the rat receives a mild electric shock from the floor.
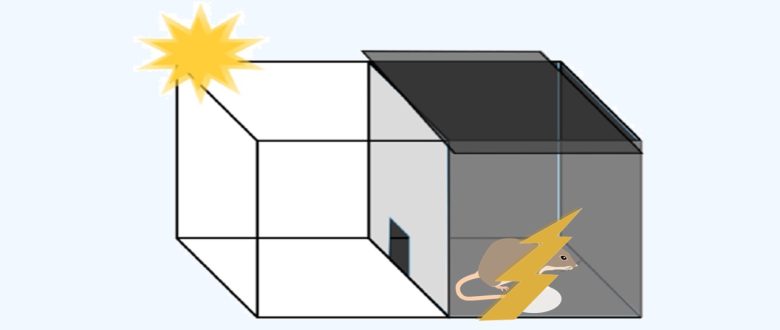
Next, as a memory test phase, the rat is placed in the same box after some time has passed.
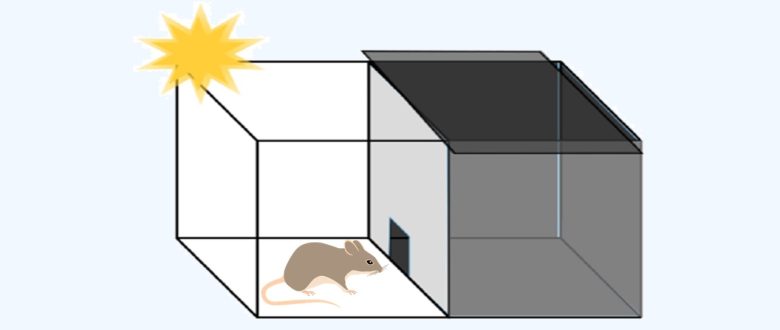
Normal rats will not like to enter dark rooms.
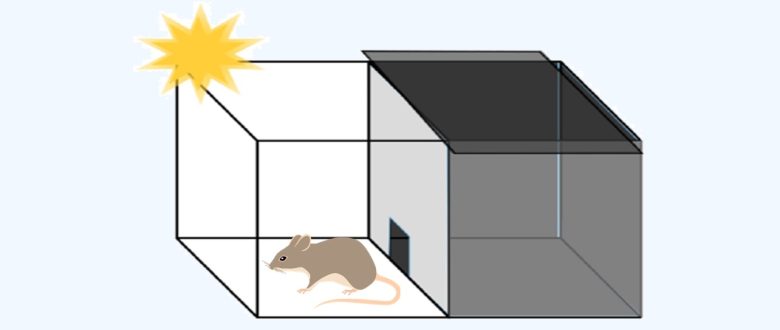
On the other hand, rats with poor memory forget that they have received an electric shock, so the time taken to enter the room becomes shorter.
Therefore, the time taken to enter the room can be used to evaluate their memory.
Decline in Memory
The time taken to enter the dark room decreased by 40 % due to the EMF exposure during pregnancy. This means that the daughter rats forgot that they had been shocked once, indicating that their memory declined.
Narayanan et al. 2009
Cell phones were placed under the floor of the breeding cages and kept on incoming calls for 50 minutes per day, and male rats aged 10-12 weeks, equivalent to adolescents, were exposed to their EMFs for 4 weeks.
Next, the rats were tested using the Morris water maze test.
As a result, the rats showed a decrease in their memory.
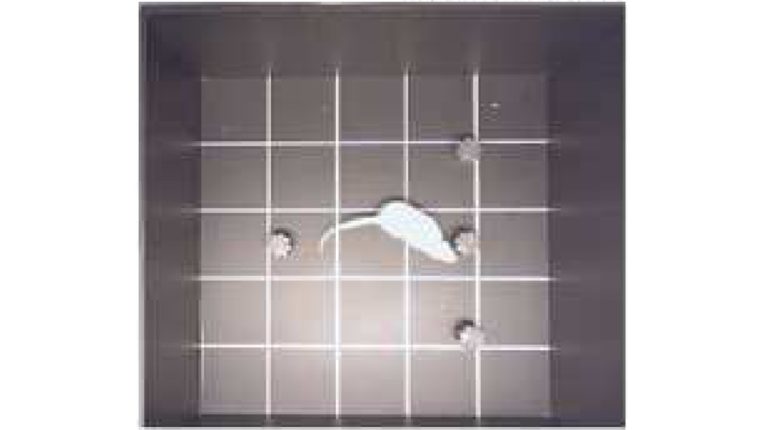
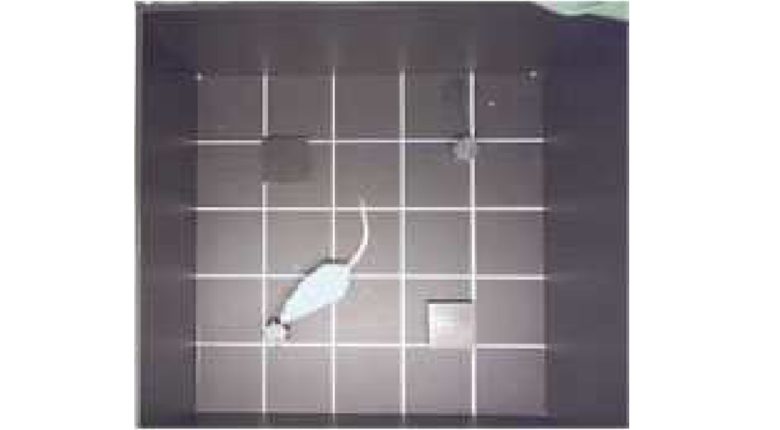
Morris Water Maze Test
The Morris water maze test is a test that evaluates spatial memory.
First, the rats are placed floating in an opaque pool.
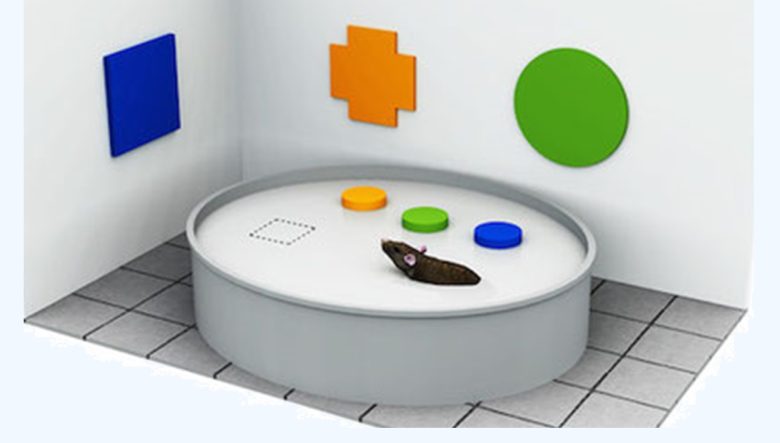

The pool has a escape platform set up invisibly so that the rat can climb up and rest when he reaches it.
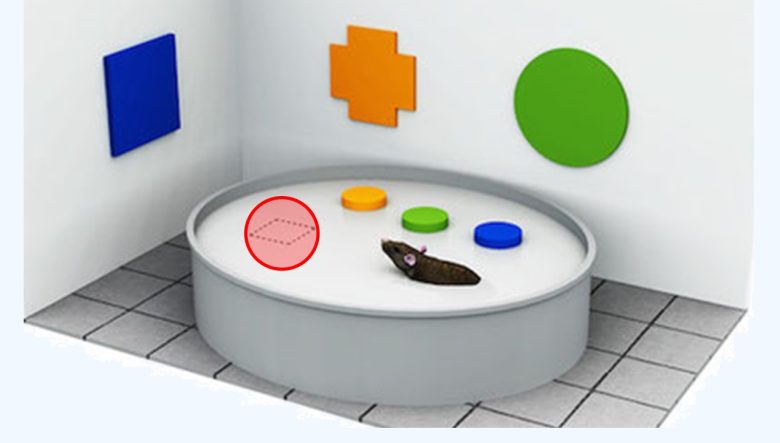

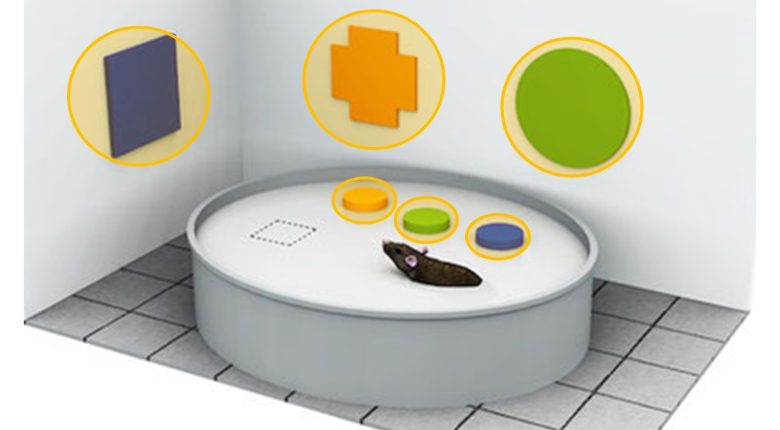
The location of the escape platform is memorized by using the shapes placed on the device as cues.

After several trainings, rats with better memories take less time to reach the escape platform.
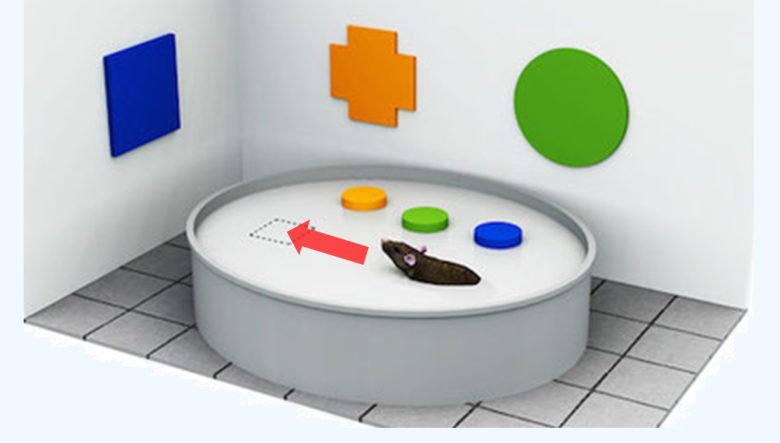

During the training phase, a total of seven training sessions is performed and the reaching time to the escape platform is measured.
Then, 24 hours after the last training, the escape platform is removed and the test is performed .
The reaching time to where the escape platform was and the staying time there are used to evaluate their memory.
Decline in Memory (Training)
No matter how many times they were trained, large difference in reaching time to the escape platform remained, indicating that rats' memory declined due to the cell phone EMF exposure.
Decline in Memory (Test)
Narayanan et al. 2010
Cell phones were placed under the breeding cages and kept on incoming calls for 38 minutes per day, and male rats aged 8-10 weeks, equivalent to adolescents, were exposed to their electromagnetic radiation for 4 weeks.
Next, the rats were tested using the passive avoidance test.
As a result, the rats showed a decrease in their memory.
Passive Avoidance Test 1
First, the rat is placed in a box divided into a dark room and a light room.
In the first step of this experiment, the electric shock in the dark room is turned off.
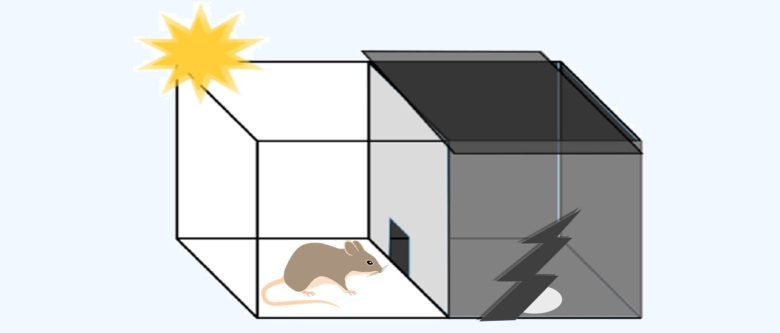
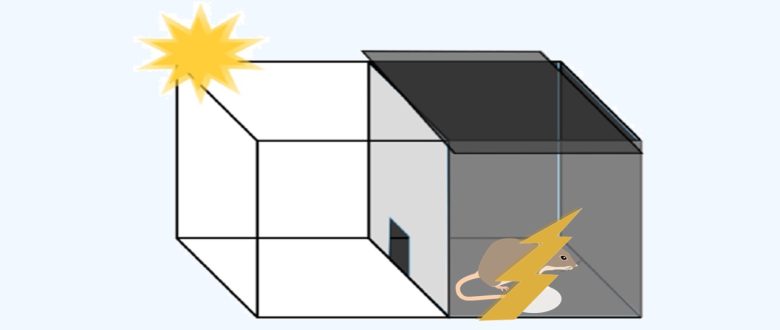
The time he takes to enter the dark room is then measured three times to evaluate his memory.
Decline in Memory
(Without Shock)
Passive Avoidance Test 2
In the next step of this experiment, the electric shock is turned on and the rats receive an electric shock once.
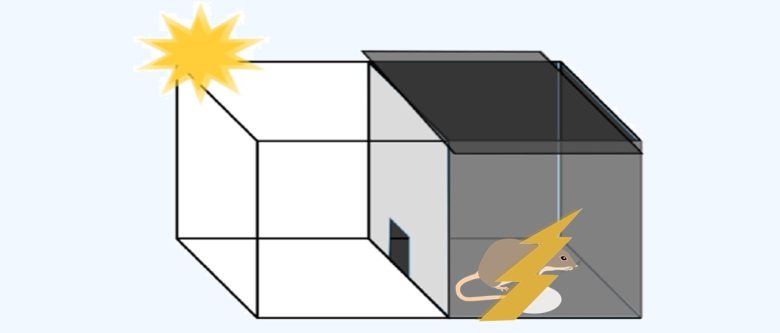
They are then placed in the box after 24 or 48 hours, and their memory is evaluated by measuring the time taken to enter the dark room.
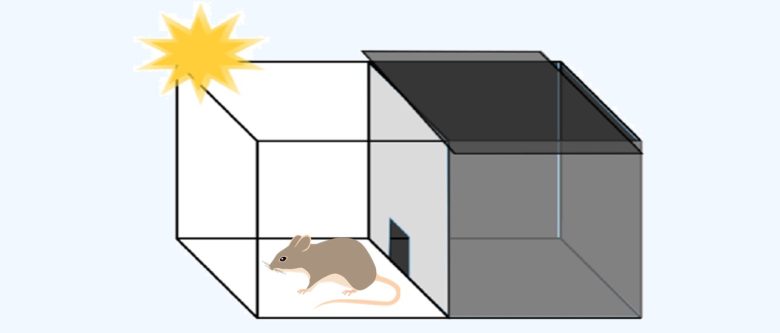
Decline in Memory
(With Shock)
The time taken to enter the dark room again decreased by 70-80% due to the cell phone EMF exposure. This means that the rats forgot that they had been shocked once, indicating that their memory declined.
Gao et al. 2017
Male mice aged 10-12 weeks, equivalent to adults, were exposed to 50 Hz ELF-EMFs with a strength of 200 μT for 8 hours per day for 30 days.
Next, the mice were tested using the Morris water maze test.
As a result, reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the brain increased, and the mice showed a decline in their memory.
Also, treatment with catechin/epicatechin, which has antioxidant properties, suppressed the damage above.
Increase in ROS
The increase in lipid peroxidation and the decrease in antioxidant activity mean the increase in ROS.
Morris Water Maze Test
First, the training for Morris water maze test is performed 4 times per day for 6 consecutive days.

Then, three hours after the last training on the 6th day, the escape platform is removed and the test is performed.
The reaching time to where the escape platform was and the staying time there are used to evaluate their memory.

Decline in Memory
Nittby et al. 2007
Rats aged 16-24 weeks, equivalent to adolescents, were exposed to cell phone EMFs at a whole-body average SAR of 0.0006 W/kg or 0.06 W/kg for 2 hours per day for 55 weeks.
Next, the rats were tested using an episodic-like memory test.
As a result, the rats showed a decrease in their memory.
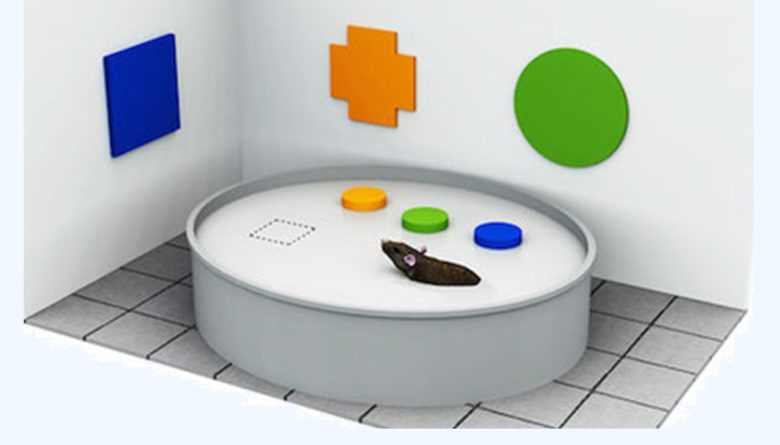
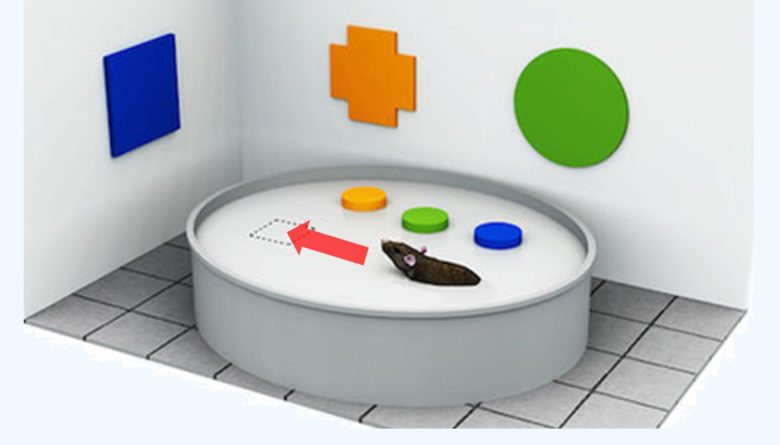
Episodic-Like Memory Test
First, as a training phase, the rats are allowed to explore 4 cubic objects.
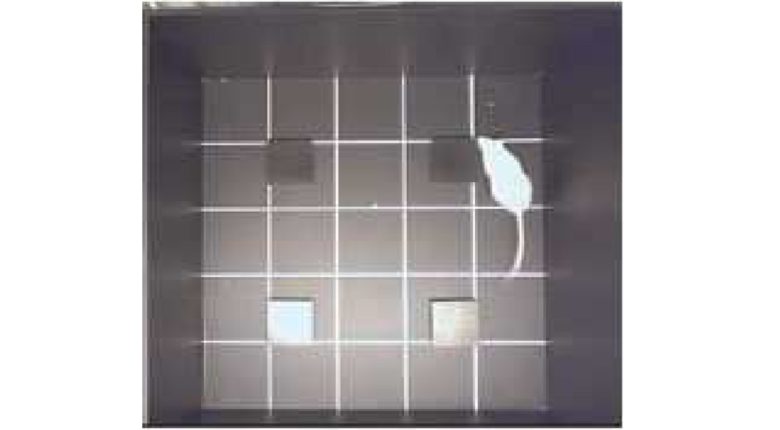
Next, after 50 minutes, they are allowed to search for the 4 cylindrical objects.

Then, after another 50 minutes, as a test phase, the 2 cylindrical objects are replaced by the 2 old familiar cublic objects and the rats are allowed to explore them.

Normal rats will explore old familiar objects longer than recent familiar objects.
This is a manifestation that the rat has a good memory of events that occurred in the past (episodes).
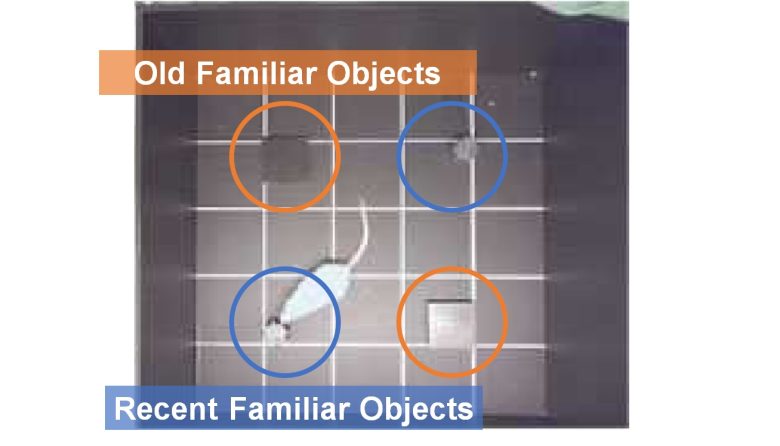
On the other hand, in rats with poor memory who have forgotten the past events, it is expected that no difference in exploration time will appear between recent familiar and old familiar objects.
The exploration times for each object are measured, and their memory is evaluated.
Decline in Memory
It is noteworthy that the EMFs from the cell phones showed biological effects even at the weak strength of 0.0006 W/kg, the whole-body average SAR.
Maaroufi et al. 2014
Male rats aged 4 weeks, equivalent to children, were exposed to 900 MHz RF-EMFs at a local SAR of 0.05-0.18 W/kg for 1 hour per day for 3 weeks.
Next, the rats were tested using the object exploration test.
As a result, the rats showed a cognitive decline.
The disturbance of neurotransmitter monoamine was also observed, which is described in the section on Neurotransmitter Dysfunction.
Object Exploration Test
One session of 4 minutes is given to the rats to explore objects, for a total of 8 sessions.
Each session has a 4-minute interval.
First, over sessions 1-5, the rats are allowed to familiarize with the same placement of the objects.
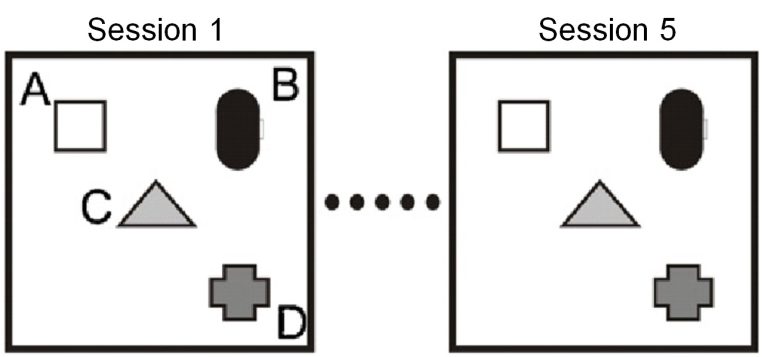
Next, in session 6, the triangular object is changed in location (spatial change).
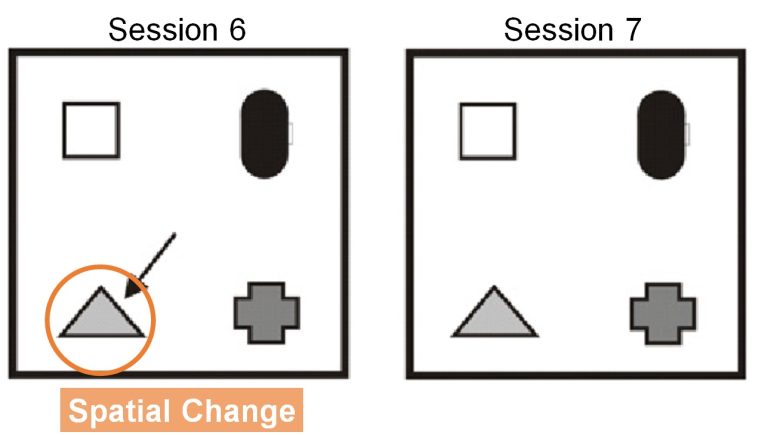
Here, before and after the spatial change, the exploration times for each triangular object are measured, and the difference between them is the exploration score.
A normal rat will explore longer for an object that has changed in location, resulting in a larger exploration score.
On the other hand, rats with cognitive decline should not be able to recognize a spatial change, and their object exploration time should remain the same, resulting in a smaller exploration score.
Also, in session 8, the rectangular object is changed to a circular object (object change).
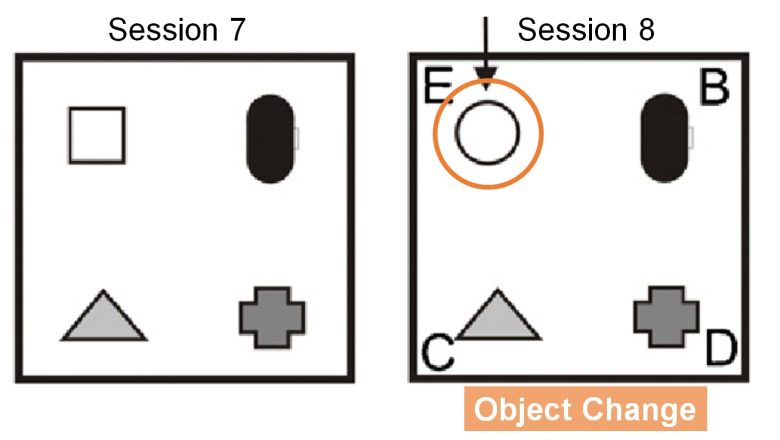
Here, the exploration time of the circular object (E) and the average exploration time of the other three objects (B, C, and D) are measured, and the difference between them is the exploration score.
Normal rats will search longer for a novel object, resulting in a larger exploration score.
On the other hand, rats with cognitive decline should not be able to recognize an object change, and their object search time should remain the same, resulting in a smaller search score.
Cognitive Decline
(Spatial Change)
The exploration score for spatial change was zero due to the EMF exposure, i.e., there was no difference in exploration times between before and after changing the object's location. This means that the rats could not recognize the spatial change at all, indicating a cognitive decline.
Cognitive Decline
(Object Change)
The exploration score for object change decreased considerably due to the EMF exposure, i.e., there was no considerable difference in search times between novel and other objects. This means that the rats were less able to recognize the object change, indicating a cognitive decline.
Rats with damaged hippocampus have been shown to be unable to recognize spatial changes. (Save et al. 1992, Lee et al. 2005)
The rats in the exposed group could not recognize the spatial change at all, indicating that it is highly likely that their hippocampus had been damaged.
Hyperactivity
Next, I will present studies showing that exposure to EMFs from cell phones and other sources caused hyperactivity in mice.

Studies
Kim et al. 2017
Mice aged 6 weeks, equivalent to children/adolescents, were exposed to RF-EMFs at 835 MHz for 5 hours per day at a local SAR of 4 W/kg for 12 weeks.
Next, the mice were tested using the open field test.
As a result, the mice showed hyperactivity.
Damage to myelin sheaths in the cerebral cortex was also observed, which is described in the section on Damage to Brains.
Open Field Test
The open field test is a test where mice are allowed to move freely in a rectangular space and their behaviors are observed.
Mice are allowed to move freely for 30 minutes, and their hyperactivity is evaluated by measuring moving distance, moving duration, and the number of standing.
Hyperactivity
Aldad et al. 2012
Cell phones with a local SAR of 1.6 W/kg were placed on top of the breeding cages and kept on an uninterrupted active call, and pregnant mice were exposed to their EMFs for 3 weeks throughout the entire pregnancy.
Next, the born-pup mice were tested using the object recognition memory test and the light-dark box test.
As a result, the mice showed decreases in memory, hyperactivity, and anxiety.
And as they grew older, they maintained this tendency.
OBJ Recognition Memory Test
On the 1st and 2nd day of testing, the mice explore two identical objects for 15 minutes.
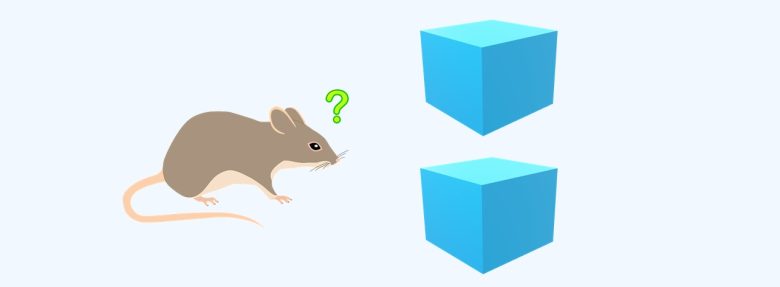
On the third day of testing, one object is replaced with a new object, and the mice explore the two objects for 15 minutes.
Here, exploration times of the two objects are measured.
Normal rats will spend more time exploring a novel object.
On the other hand, in rats with poor memory who have forgotten the familiar objects, no difference in exploring times should appear.
As a preference index, a value is defined as the exploration time for the new object divided by the exploration time for both the old and new object and multiplied by 100, which is used to evaluate the memory.
Decline in Memory
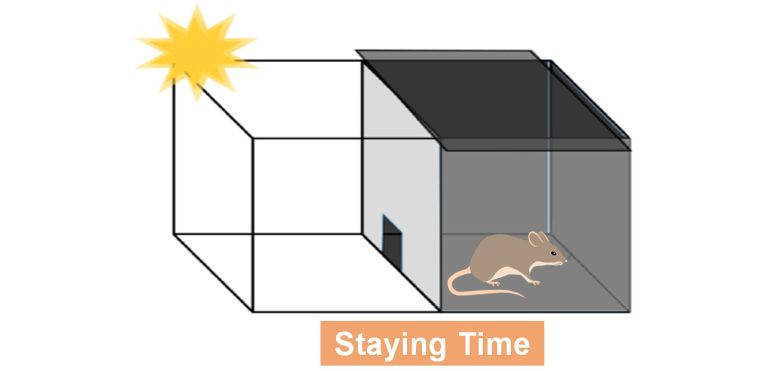
Light-Dark Box Test
A cage is divided into a dark room and a light room, and a mouse is placed in the cage.
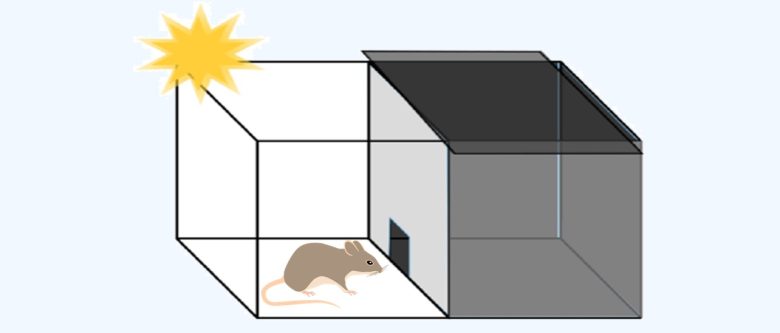
Anxiety is evaluated by the staying time in the dark room during the 5 minutes.
Hyperactivity is also evaluated by the number of transitions between the light and dark rooms during the 5 minutes.
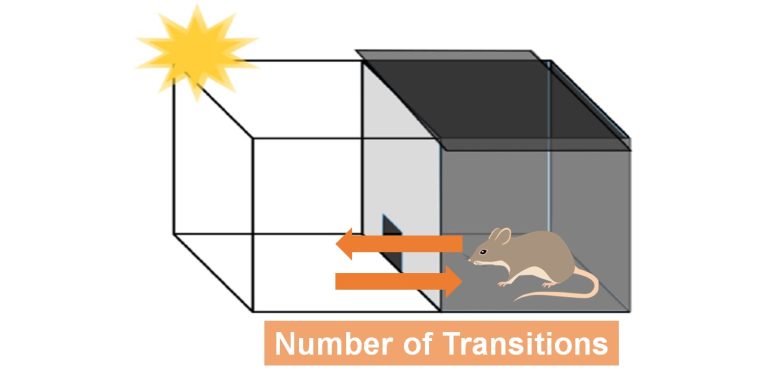
Hyperactivity
Decrease in Anxiety
Depression and Suicide
Next, I will present studies showing that depression and suicide increased with exposure to EMFs from high-voltage lines, cell phones, workplaces, and other sources.
Studies
Verkasalo et al. 1997
For adults aged 33-60 years on the Finnish twin registry, severe depression increased when they lived near high-voltage lines and when ELF-EMFs from the high-voltage lines were stronger.
Increase in Depression
On the other hand, mild depression decreased conversely.
Decrease in Mild Depression
Tamura et al. 2017
For students at a high school in Gifu, Japan, insomnia and depression increased when they spent more time per day on their cell phones.
By apps, increases were observed in the use of SNS (e.g., Facebook, Twitter, Instagram), internet searching, and online chat (e.g., Line, Skype, Kakao Talk).
Increase in Insomnia and Depression
The odds of insomnia in the high school students increased 4-fold and depression increased 2-fold with more than 5 hours of cell phone use per day.
Increase in Insomnia by Apps
The odds of insomnia in the high school students increased 3-fold with 2 hours or more of SNS use per day on their cell phones, 3-fold with Internet searches, and 3-fold with online chat.
Increase in Depression by Apps
The odds of depression in the high school students increased 4-fold with 2 hours or more of SNS use per day on their cell phones, 3-fold with Internet searches, and 3-fold with online chat.
van Wijngaarden 2000
For male employees of five large U.S. power companies, suicide increased as previous year's cumulative exposure to ELF-EMFs at workplaces increased.
This was especially more pronounced among the relatively younger groups aged under 35 or 35-49 years.
Increase in Suicide
The odds of suicide increased by 70% in the top 10% for the previous year's cumulative exposure to ELF-EMFs at the workplace.
Increase in Suicide Aged Under 35
The odds of suicide increased 2-fold in the top 50% for the previous year's cumulative exposure to ELF-EMFs at the workplace among the employees aged under 35 years.
Increase in Suicide Aged 35-49
The odds of suicide increased 4-fold in the top 50% for the previous year's cumulative exposure to ELF-EMFs at the workplace among the employees aged 35-49 years.
Baris and Armstrong 1990
For male employees of power companies in England and Wales, suicides increased when they were in occupations exposed to ELF-EMFs.
Increase in Suicide
The proportion of suicide among all causes of death increased 2-fold for radio and radar mechanics or electronic mechanics and 3-fold for telegraph radio operators.
Electromagnetic Hypersensitivity
Next, I will present studies showing electromagnetic hypersensitivity (EHS) increased with exposure to EMFs from cell towers, radio towers, and cell phones.
What is EHS?
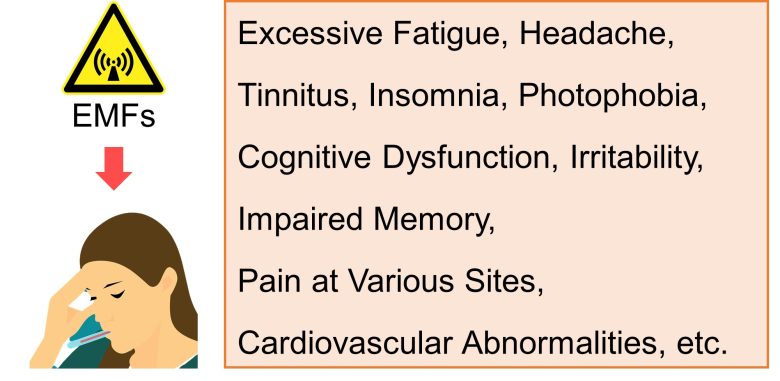
EHS is a syndrome that may include some or all of the following: excessive fatigue, headache, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), insomnia, photophobia (discomfort in bright light), a feeling of cognitive dysfunction and impaired memory, irritability, pain at various sites and often cardiovascular abnormalities. (Carpenter 2015)
EHS was known in the past as "Microwave Syndrome", and occurs following the patient's acute or chronic exposure to EMFs in the enviroment. (Stein and Udasin 2020)
Studies
Santini et al. 2002
For study participants recruited from throughout France, EHS increased as the distance from their homes to cell towers decreased.
Increase in EHS
Abelin et al. 2005
At that time, residents living near a shortwave radio transmitter in Schwarzenburg, Swiss, had filed a petition to the government, complaining about symptoms such as nervousness, headache, sleep disturbance and loss of energy.
The government agreed to investigate the situation, and this study was undertaken.
The strength of the RF-EMFs was 0.3 μW/cm2 within 0.6 mile (0.9 km) of the transmitter, 0.17 μW/cm2 between 0.9-0.6 mile (1.5-0.9 km), and 0.0004 μW/cm2 over 0.9 mile (1.5 km). (*)
It is calculated from the strength of the magnetic field described in the paper, as the impedance of free space 377 Ω.
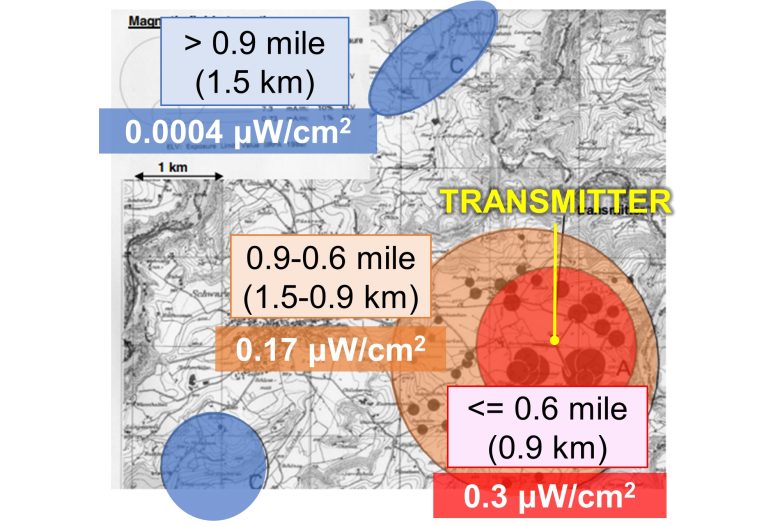
The study found that EHS increased as the distance from their homes to the shortwave radio transmitter increased.
Increase in EHS
Preece et al. 2006
Akrotiri is one of the UK Sovereign Base Areas in Cyprus and contains a military air base.
At the time, a large antenna was installed at the base, and a plan to build a new, larger antenna was proposed.
Residents voiced concerns about cancer and reproduction and called for a health survey at a public meeting.
The authorities agreed, and this study was undertaken.
The strength of RF-EMFs was 0.086 μW/cm2 in Akrotiri, 0.056 μW/cm2 in neighboring Asomatos, and 0.00002 μW/cm2 in a control village in the mountains (*)
It is calculated from the strength of the electric field described in the paper, as the impedance of free space 377 Ω.
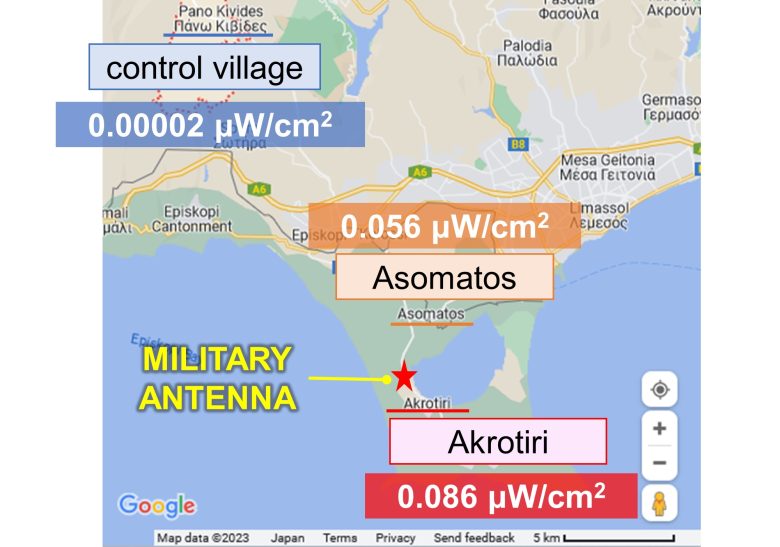
( Cited and Modified from Google Map )
The study found that EHS increased as the strength of RF-EMFs in the residential area increased.
They said no cancer or reproductive effects were shown, but no verifiable data were presented.
Increase in EHS
Sandstrom 2001
For randomly seleced users of company cell phones in southern Norway, EHS increased as the call time per day they spent on their cell phones increased.
Increase in EHS
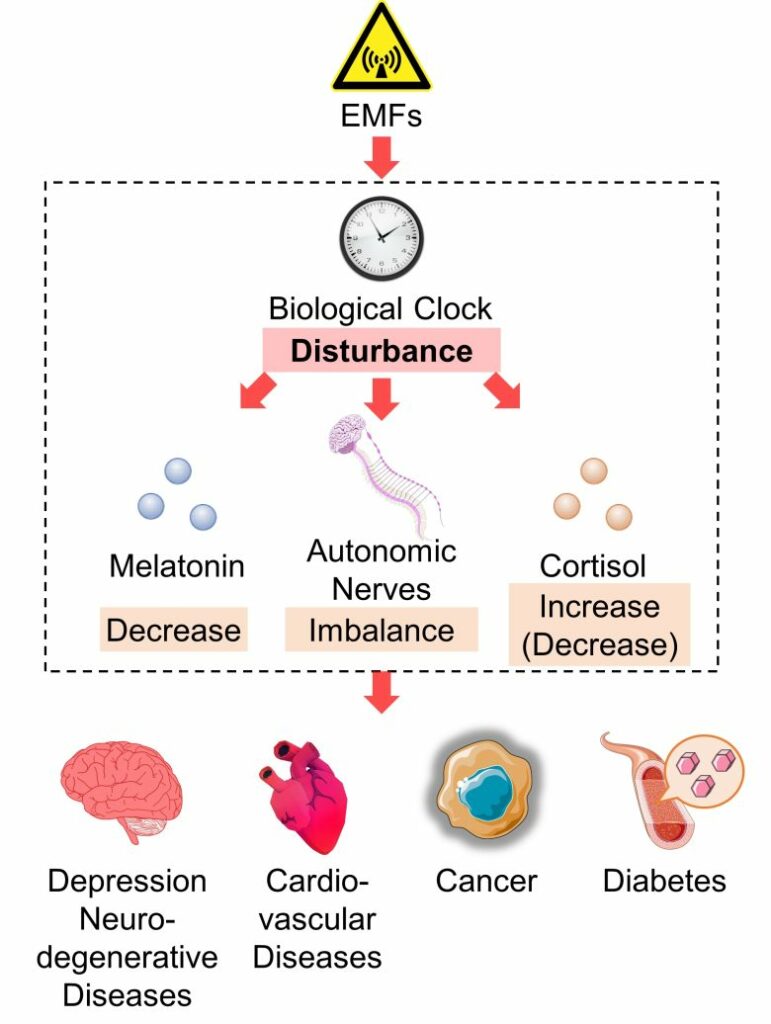
Biological Clock Disturbance
Circadian Hormone Disturbance Caused by EMFs
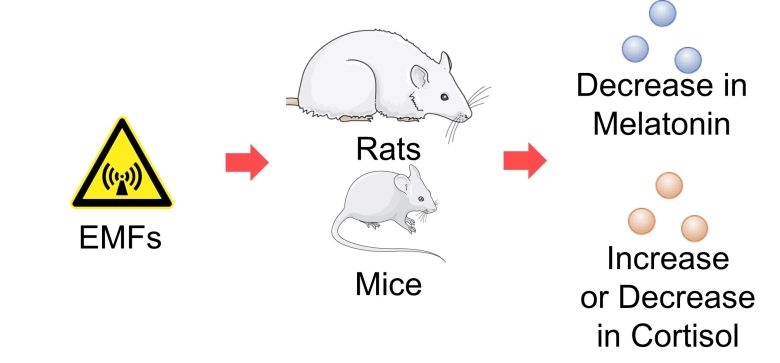
Next, I will present studies showing that melatonin decreased and cortisol increased or decreased with exposure to EMFs from cell phones, cell towers, high-voltage lines, electrical appliances and other sources.
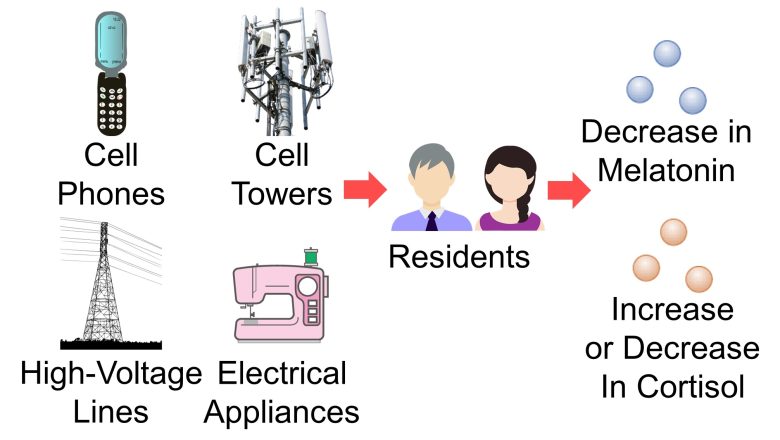
I will also present studies showing that exposure of rats and mice to EMFs decreased melatonin and increased or decreased cortisol.
What is Melatonin and Cortisol?
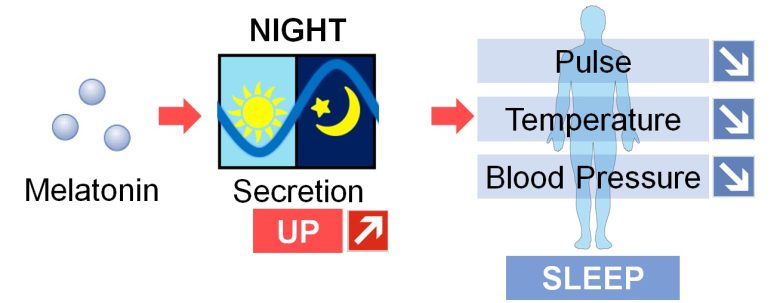
Melatonin is known as a sleep hormone that is secreted by the pineal gland by night and leads to decreases in pulse rate, body temperature, and blood pressure.
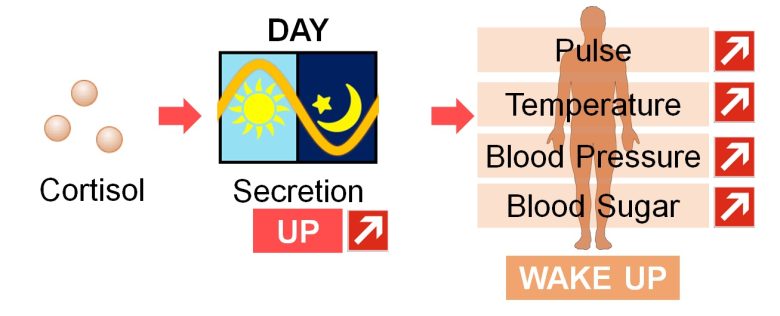
Cortisol, on the other hand, is known as a wake-up hormone that is secreted from the adrenal glands by day and leads to increases in pulse rate, body temperature, blood pressure, and blood sugar level.
Melatonin and cortisol levels fluctuate on a circadian basis (approximately 24 hours) and are therefore called circadian hormones.
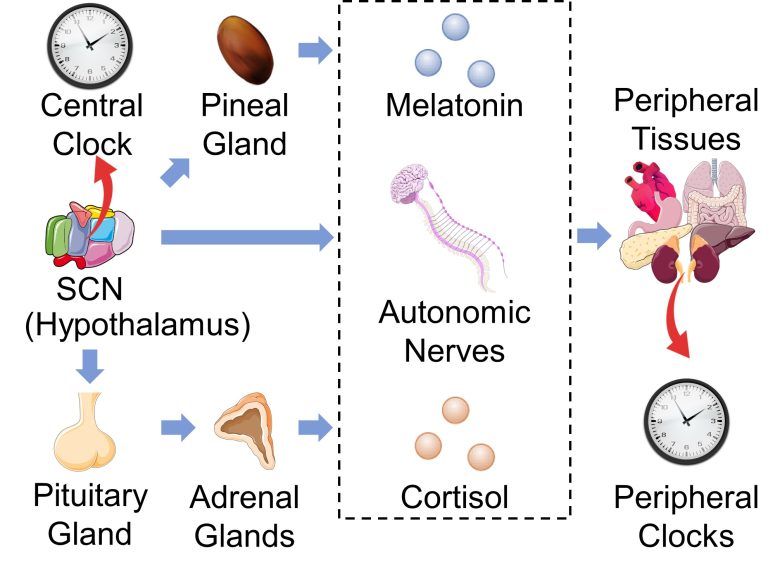
Regulation of Circadian Rhythms
The peripheral tissues of the body, such as the heart and lungs, each have their own circadian rhythms, called peripheral clocks.
In mammals, the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus regulates the circadian rhythms of these peripheral tissues, called the central clock.
The circadian rhythm of the SCN are conveyed to the peripheral tissues via the circadian hormones melatonin and cortisol, as well as via the autonomic nerves. (Menaker et al. 2013)
Biological Clock Disturbance Caused by EMFs
It has been shown that EMF exposure disturbs the circadian rhythms of melatonin and cortisol, as well as autonomic nerves.
So, you may suspect that EMFs are causing disturbance of the biological clock.
In fact, there are experiments showing that EMF exposure disturbed the circadian rhythm of the SCN in rats and also disturbed the circadian rhythms of clock genes, which are the entities responsible for circadian rhythms in cells.
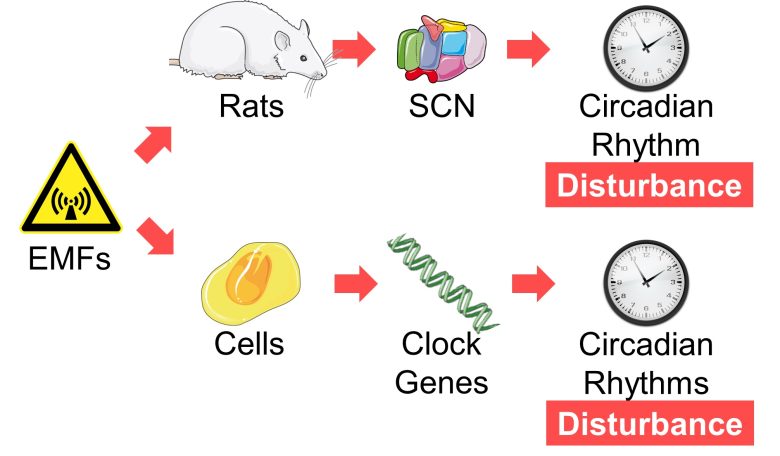
These experiments are also presented here together.
Studies of Circadian Hormone Disturbance
Jarupat et al. 2003
Female study participants aged 16-36 years in Japan, had a cordless phone (PHS) in contact with their left ear and were exposed to its EMFs for 30 minutes every 1 hour between 7:30 p.m. and 1 a.m. for a total of 3 hours.
As a result, melatonin secretion decreased at 2:00 a.m.
Decrease in Melatonin
The melatonin level in saliva decreased by 40% due to the cordless phone EMF exposure for only 3 hours at night.
Burch et al. 2000
For male employees of six U.S. power companies, nocturnal and overnight total melatonin secretion decreased as the strengh of ELF-EMFs from substations or three-phase conductors increased.
Decrease in Melatonin
Yellon 1994
Adult Djungarian hamsters were exposed to 60 Hz ELF-EMFs with a strength of 100 μT for only 15 minutes at 10:00 p.m.
As a result, nocturnal melatonin secretion drastically decreased, and the circadian rhythm of melatonin was lost.
Replication tests were performed twice, the first time replicating the result, but the second time not.
Decrease in Melatonin
Wilson et al. 1981
Rats aged 56 days, equivalent to adolescents, were exposed to 60 Hz ELF-EMFs with a strength of 65 kV/m for 20 hours per day for 30 days.
As a result, nocturnal melatonin secretion drastically decreased and the circadian rhythm of melatonin was lost.
Decrease in Melatonin
The circadian rhythm of melatonin was lost due to the EMF exposure.
Augner et al. 2010
RF-EMFs from a cell tower were adjusted to three different strengths using EMF shieldings: strong 0.21 μW/cm2, medium 0.015 μW/cm2, and weak 0.00052 μW/cm2.
Next, study participants aged 18-67 years in Salzburg, Austria, were exposed to the cell tower EMF at the following timetable.
| Clock Time | Session | Strengh |
|---|---|---|
| 9:00-9:50 | 1 | Weak |
| 9:55-10:45 | 2 | Weak |
| 10:50-11:40 | 3 | Weak |
| 11:45-12:35 | 4 | Weak |
| 12:40-13:30 | 5 | Strong |
Each session lasts 50 minutes with a 5-minute break in between.
As a result, cortisol secretion increased from session 4 to session 5.
Increase in Cortisol
Practically speaking, the cortisol level in saliva increased by 40% due to the cell tower EMF exposure for only 50 minutes.
Mortazavi et al. 2012
For dentists and dental students at Rafsanjan University of Medical Sciences, Iran, cortisol secretion decreased in the morning and at noon, especially at noon, when they used EMF-emitting scalers on daily duty.
Decrease in Cortisol
The cortisol level in blood in the morning decreased by 20% and at noon decreased by 40% with the use of EMF-emitting scalers.
Studies of Biological Clock Disturbance
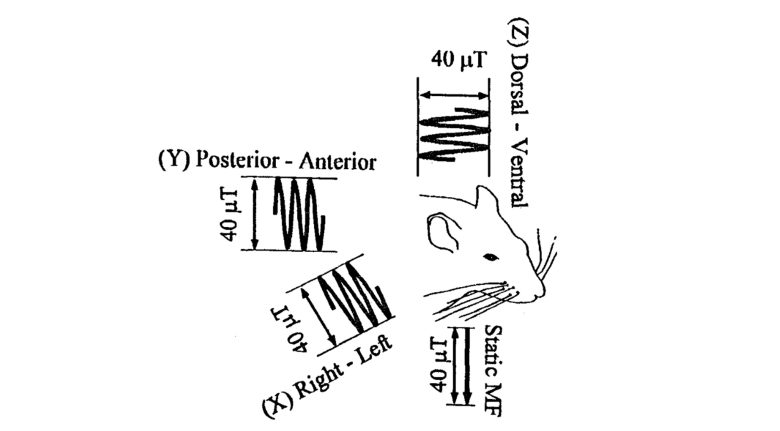
Hiwaki
Female rats were exposed to 50 Hz ELF-EMFs with a strength of 40 μT for 48 hours from three directions: horizontal/sideways (X), horizontal/longitudinal (Y), and vertical (Z).
In addition to EMFs, a static magnetic field of 40 μT was applied in the vertical (Z) direction.
As a result, during the exposure period, the circadian rhythm of the rat's SCN was disturbed depending on the irradiation direction.
Circadian Rhythm of the SCN
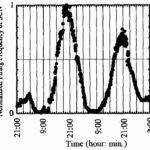
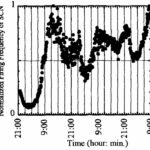
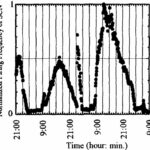
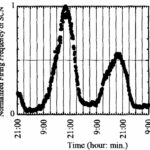
The circadian rhythm of the SCN was lost during x-directional irradiation, the cycle of the circadian rhythm was shortened during y-directional irradiation, and no significant change was observed during z-directional irradiation.
Thöni et al. 2021
Mouse fibroblasts, which are skin-producing cells, were exposed to EMFs that generate nuclear magnetic resonance for 6 or 12 hours (*).
A treatment device using nuclear magnetic resonance called MBST ® generates a static magnetic field of 0.4 mT and EMFs with a resonance frequency of 17 kHz.
As a result, the circadian rhythms of mRNA and proteins produced by clock genes were disturbed.
This was especially more pronounced for the 6-hour exposure group.
Disturbance of Circadian Rhythm
(mRNA)
Disturbance of Circadian Rhythm
(Proteins)
Consequences of Circadian Hormone Disturbance
We have seen that EMF exposure can decrease melatonin secretion and increase or decrease cortisol secretion.
And these circadian hormone disturbance are known to correlate with various diseases.
Insomnia
Decreased nocturnal melatonin secretion has been shown in insomnia patients. (Riemann et al. 2002, Hajak et al. 1995, Haimov et al. 1994)
Melatonin deficiency is suggested as a cause rather than a marker for insomnia in the elderly. (Cardinali et al. 2012)
A study found that evening and nocturnal cortisol levels were significantly increased in insomnia patients. (Rodenbeck et al. 2002)
Depression
Disturbances in sleep and circadian rhythms are prominent features of depression. (Cardinali et al. 2012)
In most cases of mood disorders including depression, insomnia appeared before than mood disorder symptoms. (Ohayon and Roth 2003)
In an epidemiological study of young adults, the incidence of major depression in persons with a history of insomnia increased 4-fold. (Breslau et al. 1996)
Depression is associated with flattening of the diurnal cortisol curve. (Joseph and Golden 2016)
Suicide
It was found that the patients with hypersomnia and insomnia had significantly higher scores on a suicide scale and were significantly more likely to become suicidal than those without sleep disturbance. (YoEargon et al. 1997)
Breast Cancer
It is well documented that melatonin has a significant anti-tumor activities and several studies have demonstrated the inverse correlation between melatonin levels and the risk of breast cancer (the less the melatonin, the more the risk of breast cancer). (Kubatka et al. 2018)
Hippocampal Atrophy
Increased cortisol secretion is known to degenerate and atrophy the hippocampus.
The long-term cortisol (corticosterone) administration to rats induced morphological deterioration in the hippocampus of the brain, and cognitive impairment. (Arbel et al. 1994)
In Cushing's syndrome, a syndrome due to prolonged exposure to cortisol, patients show diminished hippocampal size and verbal recall inversely related to cortisol levels. (Stokes 1995)
A depression associated with hippocampal atrophy typically involve significant excessive secretion of cortisol (glucocorticoids) (Lee et al. 2002).
Alzheimer's Disease, ADHD, Depression
Elevated cortisol levels may exert detrimental effects on cognition and contribute to Alzheimer's disease pathology. (Ouanes and Popp 2019).
It has been shown that the pathology of Alzheimer's disease begins with hippocampal atrophy, that the volume of the hippocampus is reduced in children with ADHD, and that the hippocampus is also atrophied in depression. (Dhikav and Anand 2011, Hoogman et al. 2017, Videbech 2004)
Type 2 Diabetes
Poor quality sleep is associated with a number of chronic conditions including type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, hypertension. (Abell et al. 2016)
Flattening of the diurnal cortisol curve is associated with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. (Joseph and Golden 2016)
Stress-Associated Disorders
Stress has been associated with increased activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, (GUNNAR and VAZQUEZ 2001), and is accompanied by a consequent increase in cortisol levels.
However, several stress-associated disorders, notably PTSD and chronic pain and fatigue syndromes, paradoxically exhibit somewhat low blood levels of the stress hormone cortisol. (Yehuda and Seckl 2011)
It is hypothesized that chronic activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis precedes this phenomenon. (GUNNAR and VAZQUEZ 2001)
So, in another word, chronic activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis may lead to the development of several stress-associated disorders, which manifest themselves in the form of lower cortisol levels.
Consequences of Biological Clock Disturbance
Biological clock disturbance has been linked to depression, cancer, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, etc. (Salgado-Delgado et al. 2011, Leng et al. 2019, Gery and Koeffler 2010, Parameswaran and Ray 2021, Takeda and Maemura 2011), many of which overlap with diseases involving circadian hormone disturbance and autonomic imblance.
You can assume that biological clock disturbance leads to circadian hormone disturbance and autonomic imbalance and that the synergistic effects of these factors cause various diseases.
Neurotransmitter Dysfunction
Next, I will present studies showing that exposure to EMFs from cell phones and other sources causes neurotransmitter dysfunction in rats, i.e., disturbance of neurotransmitter monoamines.
What are Monoamines?
Neurotransmitters are substances used to transmit signals between neurons, the brain's main information-processing entity.
Monoamine is a generic term for neurotransmitters that share the common chemical structure of having one amino group.
The monoamines serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine have a great impact on mood, emotion and behavior. (Lövheim 2012)
And as will be described later, monoamine disturbances may lead to aggressive behavior, suicide, and other problems.
Studies
Megha et al. 2015
Male rats were exposed to RF-EMFs of 900 MHz and 1800 MHz at whole-body average SARs of 0.00059 W/kg and 0.00058 W/kg, respectively, for 2 hours per day for 30 days.
As a result, monoamines serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and adrenaline decreased in the hippocampus as the cell phone frequency increased.
Decrease in Monoamines
Maaroufi et al. 2014
Male rats aged 4 weeks, equivalent to children, were exposed to 900 MHz RF-EMF at a local SAR of 0.05-0.18 W/kg for 1 hour per day for 3 weeks.
As a result, monoamines dopamine and serotonin decreased in the hippocampus and basal ganglia, but increased in the cerebellum and prefrontal cortex.
A decline in memory was also observed, which is described in the section on Decline in Memory.
Decrease in Monoamines
Increase in Monoamines
Ismail et al. 2015
Smartphones with a local SAR of 1.00 W/kg were placed 10 cm away from breeding cages and were on incoming calls 15 times per day, and pregnant rats were exposed to their EMFs for 3 weeks throughout the entire pregnancy, and then the born-pup rats were exposed for another 4 weeks (equivalent to infancy).
As a result, monoamines serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and adrenaline were disturbed in the brain, and the sleep hormone melatonin also decreased.
Decrease in Serotonin
The serotonin level in the brain decreased due to the smartphone EMF exposure during the fetushood and infancy.
Increase/Decrease in Dopamine
The dopamine level in the brain increased and decreased due to the smartphone EMF exposure during the fetushood and infancy.
Increase in Norepinephrine
The norepinephrine level in the brain increased due to the smartphone EMF exposure during the fetushood and infancy.
Increase in Adrenaline
The adrenaline level in the brain increased due to the smartphone EMF exposure during the fetushood and infancy.
Decrease in Melatonin
The melatonin level in the brain decreased due to the smartphone EMF exposure during the fetushood and infancy.
Burchard et al. 1998
Non-lactating Holstein cows were exposed to 60Hz ELF electric fields with a strength of 10 kV/m and 60 Hz ELF magnetic fields with a strength of 30 μT for 21.5 hours per day for 30 days.
As a result, the monoamines serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine decreased during the last 3 days of the exposure period, compared to the 3 days before the start of the exposure, and recovery trends were observed in the 3 days 5 days after the end of exposure.
Also, increases in β-endorphin and quinolinic acid were observed.
Decrease in Monoamines
Increase in β-Endorphin
The level of β-endorphin in the cerebrospinal fluid increased by 20% during the EMF exposure period. A recovery trend was seen a few days after the exposure.
Endorphins are endogenous opioids and are naturally produced in response to pain. Their principal function is to inhibit the communication of pain signals and produce a feeling of euphoria very similar to that produced by other opioids. (Jain et al. 2019)
Increase in Quinolinic Acid
The level of quinolinic acid in the cerebrospinal fluid increased 2.4-fold during the EMF exposure period. A recovery trend was seen a few days after the exposure.
Increased quinolinic acid has been observed in neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, ALS, and HIV-related cognitive decline. (Hestad et al. 2022)
Consequences of Neurotransmitter Dysfunction
We have seen that EMF exposure causes neurotransmitter dysfunction, i.e., disburbance of neurotransmitter monoamine.
And disturbance of monoamine, particularly a decrease in serotonin, have been linked to aggressive behavior and suicide.
Aggressive Behavior
Aggressive behavior in humans and animals involves changes in metabolism, primarily of serotonin and, to a lesser extent, dopamine and norepinephrine. (Brunner et al. 1993)
Researchers have emphasized the importance of decreased neurotransmission by serotonin and increased neurotransmission by dopamine and norepinephrine. (Brunner et al. 1993)
In a kindred where several men showed abnormal aggressive behavior, such as impulsive aggression, arson, attempted rape, exhibitionism, and suicide attempts, a decrease in metabolites of serotonin and dopamine and an increase in metabolites of norepinephrine were observed. (Brunner et al. 1993)
In this kindred, a protein involved in monoamine metabolism (monoamine oxidase) was genetically defective. (Brunner et al. 1993)
Mice genetically engineered to lose the same protein also showed aggressive behavior. When these mice were treated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), i.e., serotonin levels in their brain were increased, the mice's aggressive behavior decreased. (Godar et al. 2014)
Mice that had lost their aggression completely after more than 50 generations of selection had higher levels of serotonin in their brains than their extremely malicious conspecifics. (Popova 2008)
Therefore, disruption of monoamines, especially a decrease in serotonin, due to EMF exposure can cause aggressive behavior.
Suicide
Impulsivity and aggression are highly correlated with suicidal behavior. (Gvion and Apter 2011)
In fact, it has been shown that serotonin levels are decreased in suicides and attempted suicides, and this was especially more pronounced in violent suicide. (Träskman 1981, Brown et al. 1982, MANN et al. 1990, Alvarez et al. 1999, Placidi et al. 2001)
Therefore, disruption of monoamines, especially a decrease in serotonin, due to EMF exposure can cause suicide.
Depression
In addition to this, decreases in serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine are said to lead to depression, known as the monoamine hypothesis. (Delgado 2000)
Improvement of Brain Activity
So far, I have presented studies showing the adverse effects of EMFs on the brain.
On the other hand, however, therapeutic applications of EMFs do exist. Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), for example, has fairly consistent statistical evidence as a treatment for depression. (Loo and Mitchell 2005)
There is a technique called neurofeedback, which improves brain activity while receiving visual and auditory feedback to achieve the desired EEG state. (Center for Brain Training)
A 2010 study showed that TMS-induced cortical responses are significantly enhanced after this neurofeedback. (Ros et al. 2010)
The effects of these EMFs and other means on the brain activity will be covered in detail in the next article.