Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Death

Next, I will explain a pathway by which reactive oxygen species (ROS) damage DNA and further arrest the cell cycle, leading to cell death.
I will then present studies showing that EMFs did indeed induce cell death from cell cycle arrest.
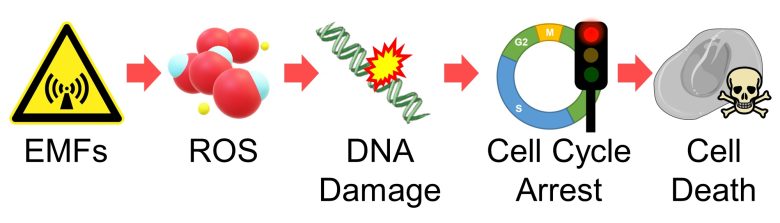
Table of ContentsAll_Pages
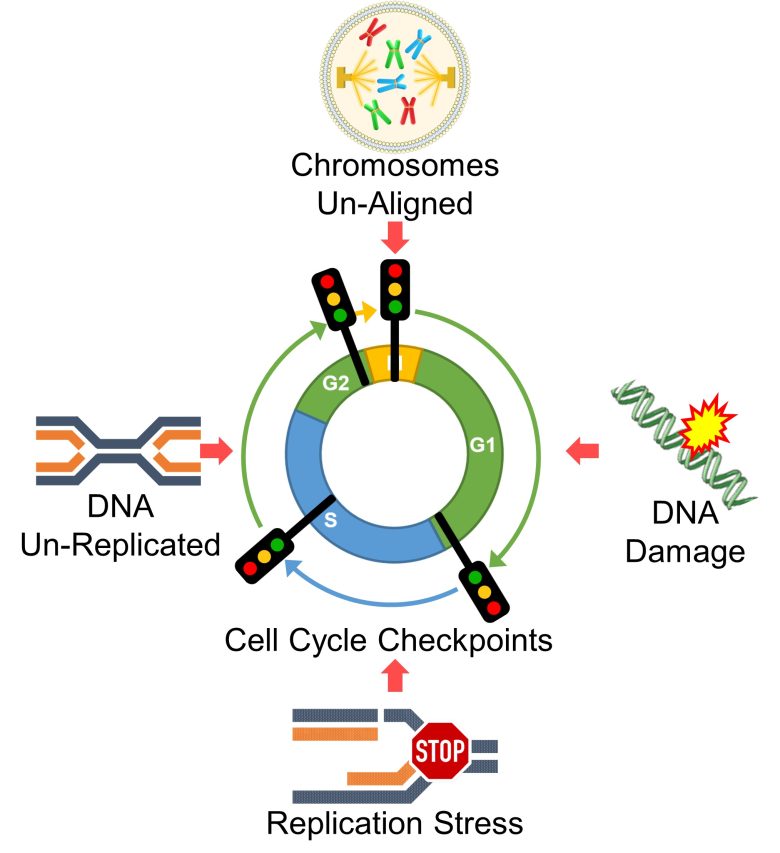
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
On the previous pages, I explained that ROS cause DNA damage, replication stress, resulting in mutations.
In reality, however, there are mechanisms in place to prevent this from happening by arresting the cell cycle in response to DNA damage, replication stress, etc., attempting to repair DNA, or at worst, causing cell death and preventing the propagation of genetic abnormalities.
These mechanisms are called cell cycle checkpoints and they are located throughout the cell cycle.
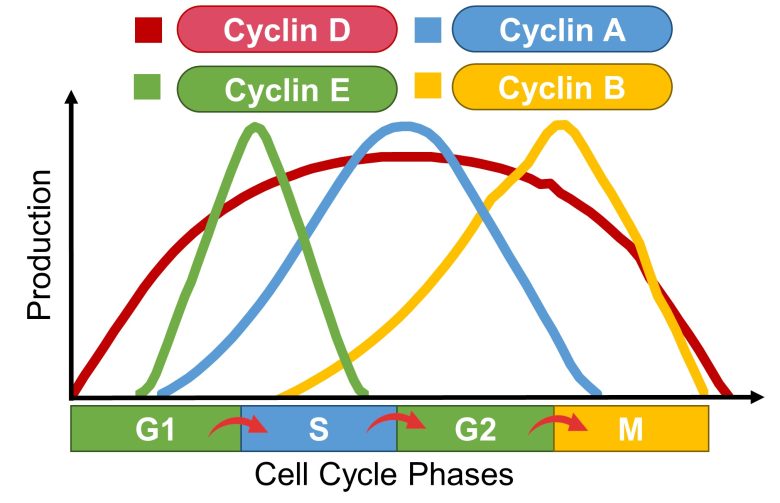
Cyclins
Cell cycle progression requires increased production and further activation of proteins called cyclins.
Increased production of cyclins D and E is required for progression from G1 to S phase, cyclin A for progression to S phase, and cyclin B for progression from G2 to M phase. (Burhans and Heintz 2009)
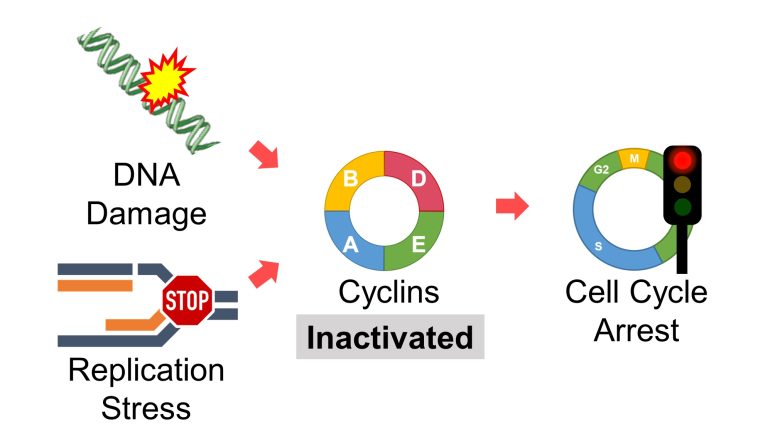
Then, in the event of DNA damage, replication stress, etc., these cyclins are inactivated and cell cycle progression is arrested.
DNA Damage Response
Among the cell cycle checkpoints, the mechanism that stops the cell cycle in response to DNA damage and replication stress is called the DNA damage response.
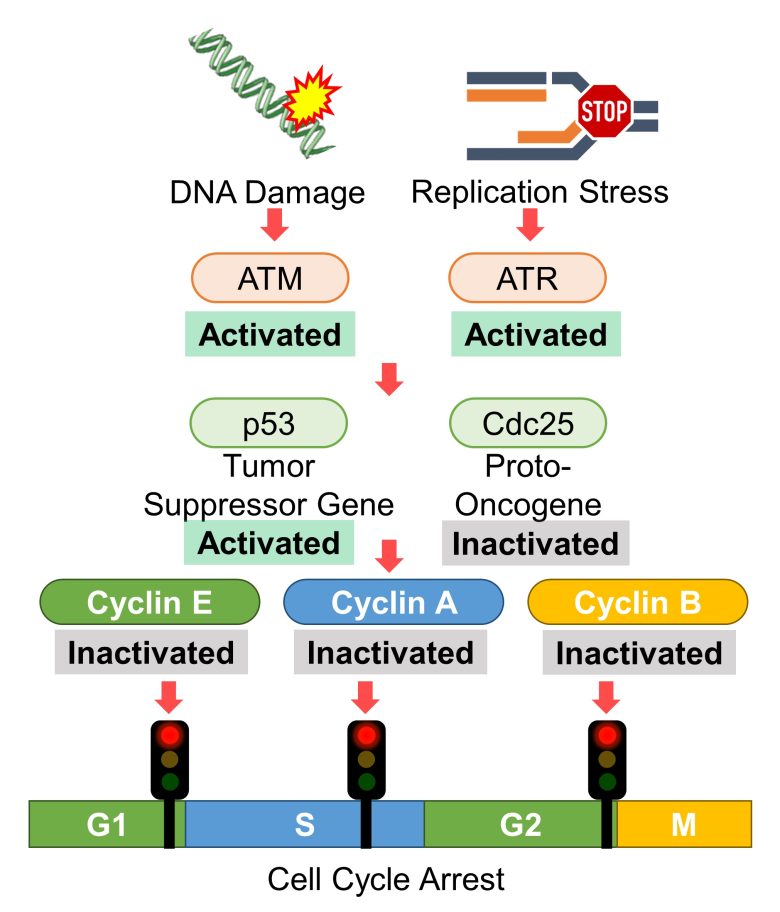
DNA Damage Response
( Cited and Modified from Rastogi et al. 2010 )
- The proteins called ATM and ATR are activated in response to DNA damage and replication stress, respectively.
- Then, proteins that arrest the cell cycle, such as tumor suppressor gene p53, are activated.
- In addition, proteins that progress the cell cycle, such as proto-oncogene Cdc25, are inactivated.
- In response, cyclins E/A/B are inactivated and the cell cycle is arrested.
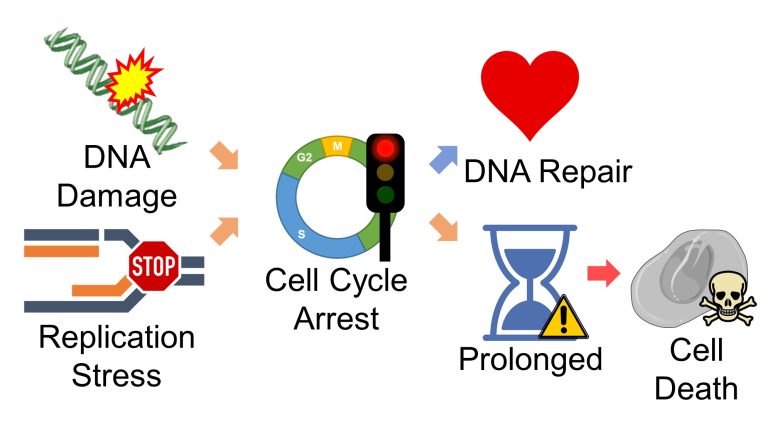
During the cell cycle arrest, DNA repair is attempted. (Burhans and Heintz 2009)
However, prolonged cell cycle arrest leads to cell death. (Burhans and Heintz 2009)
ROS Level and Duration
The effect of ROS on cells depends on their level and duration. (Boonstra and Post 2004)
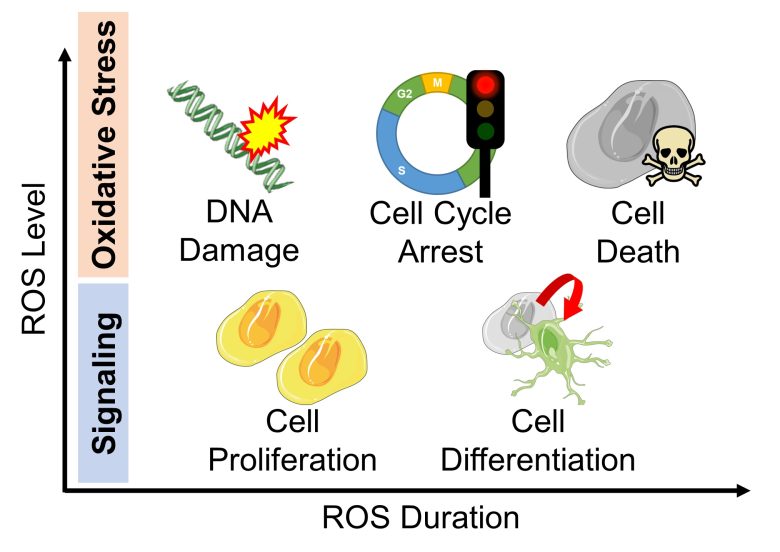
Effect of ROS Level and Duration on Cells
( Cited and Modified from Boonstra and Post 2004 )
- When ROS are at low levels, they play a role in signaling, resulting in cell proliferation by short duration, and cell differentiation, etc., by long duration.
- When ROS are at high levels, it is oxidative stress; DNA is damaged and the cell cycle is arrested. Prolonged oxidative stress leads to cell death.
Cell Death due to Prolonged Cell Cycle Arrest
I will wrap up the topic.
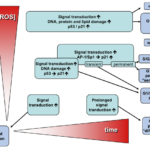
Prolonged oxidative stress leads to prolonged cell cycle arrest, and it eventually leads to cell death.
Also, prolonged exposure to EMFs inevitably leads to prolonged oxidative stress.
Therefore, we can draw the conclusion that cells die when exposed to EMFs over a prolonged period.
Cell Cycle Mechanisms are Not Perfect
Cell cycle checkpoints prevent the propagation of genetic abnormalities, but the mechanisms are not perfect.
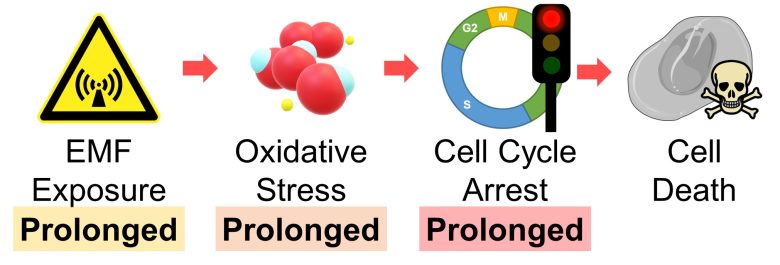
First, if the gene that constitutes cell cycle checkpoints itself becomes dysfunctional due to mutations, the checkpoint will no longer function.
For example, I mentioned on the previous page that mutations in tumor suppressor gene p53 can lead to cancer, one of the reasons being that p53 constitutes cell cycle checkpoints.
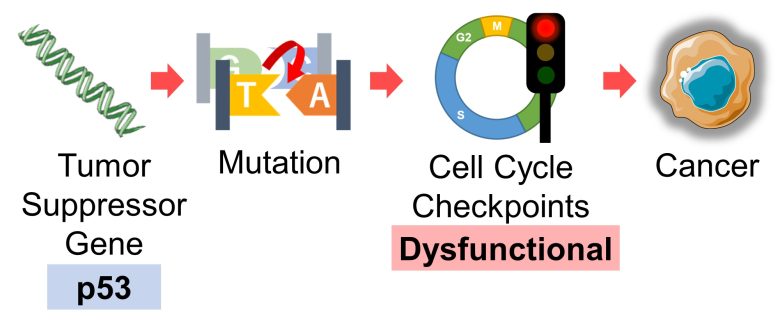
Also ,a 2013 French study found that when replication stress is mild, the cell cycle proceeds without arrest, and cells enter cell division with DNA unreplicated, resulting in chromosome breaks. (Koundrioukoff et al. 2013)
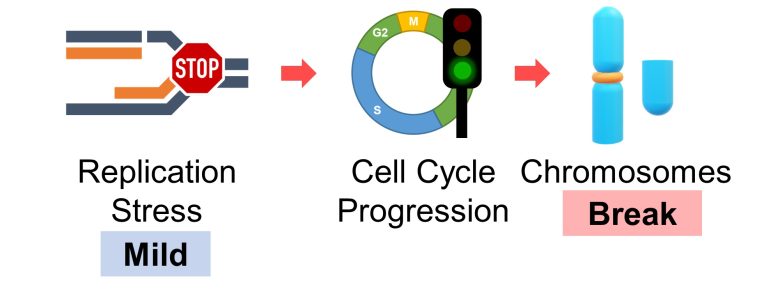
Also, a 2002 UK study found that after DNA was damaged by gamma-ray irradiation to stop the cell cycle, continuous EMF exposure caused the cell cycle to proceed conversely. (Harris et al. 2002)
This suggests that EMFs has the effect of attenuating cell cycle checkpoints.
This is probably due to the fact that EMFs cause not only an increase in ROS but also biological clock disturbance.
Biological clocks in cells are circadian rhythms set by clock genes. Since these clock genes are also components of cell cycle checkpoints (Sancar et al. 2010, Khapre et al. 2010), disturbance in the circadian rhythms of the clock genes is likeky to lead to dysfunction of the cell cycle checkpoints.
If a mutated cell survives by sneaking through cell cycle checkpoints, it is likely to have more severe consequences, such as cancer, infertility, miscarriage, genetic disorders, and more.
Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Death by EMFs
Here, I will present studies showing that the cell cycle was arrested with EMF exposure, resulting in cell death.
Studies
Xing et al. 2016
Mouse embryonic fibroblast, skin-producing cells, were exposed to 1800 MHz RF-EMFs with a strengh of 121 μW/cm2 for 48 hours.
As a result, DNA damage increased, production of p53, a tumor suppressor gene, increased, and cell death increased.
We can assume a pathway in which p53 increased in response to DNA damage, resulting in cell cycle arrest and finally cell death.
Also, treatment with N-acetylcysteine (NAC), which has antioxidant properties, suppressed the damage above.
Increase in DNA Damage
The percentage of cells with DNA damage increased from 0% to 60% due to 48 hours of EMF exposure. NAC, which has antioxidant properties, suppressed it.
Increase in Production of p53
The protein level of p53, a tumor suppressor gene, increased 2-fold due to 48 hours of EMF exposure. NAC, which has antioxidant properties, suppressed it, which is likely to be the result of suppressing DNA damage.
Increase in Cell Death
The cell death marker increased 4-fold due to 48 hours of EMF exposure. NAC, which has antioxidant properties, suppressed it.
Huang et al. 2014
Immortalized human keratinocytes, skin cells in the epidermis (*), were exposed 60 Hz ELF-EMFs with a strength of 1.5 mT for 144 hours.
The epidermis is the outer layer of skin.
As a result, the cell cycle was arrested, and cell growth was inhibited.
Cell Cycle Arrest
Cells in the G0/G1 phases increased and cells in the S and G2/M phases decreased due to the EMF exposure. It means that the cell cycle was arrested.
Inhibition of Cell Growth
The number of cell colonies decreased by 20% due to the EMF exposure. It means that cell growth was inhibited.
Liu et al. 2003
Mice were exposed to 50 Hz ELF-EMFs with a strength of 200 μT for 2 weeks.
As a result, in liver and brain cells, the cell cycle was arrested, and cell death increased.
Cell Cycle Arrest
Increase in Cell Death
Kesari et al. 2011
Cell phones with a local SAR of 0.9 W/kg were placed on standby, and male rats aged 10 weeks, equivalent to adolescents, were exposed to their EMFs in close proximity for 2 hours per day for 35 days.
As a result, in the semen, ROS increased, the cell cycle was arrested, and cell death increased.
Increase in ROS
An increase in lipid peroxidation and a decrease in antioxidant activity mean an increase in ROS.
Cell Cycle Arrest
Cells in G0/G1 phase, S phase, and G2/M phase decreased due to the cell phone EMF exposure. It means that the cell cycle was arrested.
Increase in Cell Death
The percentage of cell death increased 2-fold.
Salem 2008
CRT televisions were placed and adult male rats were exposed to their EMFs at a distance of 1 foot (30 cm) for 6 hours per day for 2 months.
As a result, cell proliferation was inhibited and cell death increased in the epidermis (*), and the thickness of the epidermis and dermis (*) decreased.
The epidermis is the outer layer of skin, and the dermis is the middle layer.
Also, treatment with vitamin A, which has antioxidant properties, suppressed the damage above.
Inhibition of Cell Proliferation
The cell proliferation marker in the epidermis decreased by 40% due to the CRT television EMF exposure. Vitamin A, which has antioxidant properties, suppressed it.
Increase in Cell Death
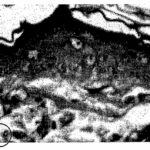
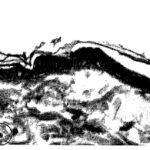
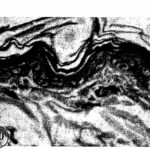
Due to the CRT television EMF exposure, cell death increased in the epidermis. Vitamin A, which has antioxidant properties, suppressed it.
Decrease in Skin Thickness
Pandey et al. 2016
Male mice aged 8-10 weeks, equivalent to adolescents, were exposed to RF-EMFs similar to those emitted from cell phones for 4 or 8 hours per day for 35 days.
As a result, DNA breaks increased and the cell cycle was arrested in the testes, sperm count decreased, and sperm abnormalities increased as the exposure time per day to the RF-EMFs increased.
The damage above recovered to some extent as the time passed after the exposure.
The comet assay is used to detect DNA breaks. In the comet assay, the more the DNA breaks, the more the tail DNA, the less the head DNA, and the larger the olive tail moment.
Increase in DNA Breaks
Cell Cycle Arrest
Decrease in Sperm Count
Increase in Sperm Abnormality
Bin-Meferij and El-Kott 2015
Test cell phones with a local SAR of 0.96 W/kg were placed in the center of breeding cages, and male rats aged 2 months, equivalent to adolescents, were exposed to their EMFs for 1 hour per day for 7 weeks.
As a result, ROS in blood increased, cell proliferation was inhibited in the testes, and sperm count decreased.
Also, treatment with moringa, which has antioxidant properties, suppressed the damage above.
Increase in ROS
An increase in lipid peroxidation and a decrease in antioxidant activity mean an increase in ROS.
Inhibition of Cell Proliferation 1

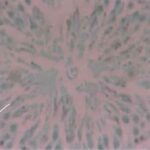
Due to the exposure to the cell phone EMFs, cells in proliferation decreased.
Inhibition of Cell Proliferation 2
The cell proliferation marker decreased by 30% due to the exposure to the cell phone EMFs. Also, the moringa, which has antioxidant properties, suppressed it.
Decrease in Sperm Count
The sperm count decreased by 60% due to the exposure to the cell phone EMFs. Also, the moringa, which has antioxidant properties, suppressed it.
That's all for the presentation of the studies.
We have confirmed that EMFs can indeed arrest the cell cycle and cause cell death.

Cell Cycle Progression by EMFs
Here is the study I mentioned earlier showing that EMFs caused the cell cycle to progress conversely.
A Study
Harris et al. 2002
Human cervical cancer cells were exposed to gamma rays at strengths of 1, 3, and 5 Gy, 4 hours after the start of the S phase. They were then continuously exposed to 50 Hz ELF-EMF with a strength of 2 mT.
As a result, 13 hours after the start of the S phase (*), the percentage of cells in the G2/M phase decreased and the percentage of cells in the next G1 phase increased. In other words, EMFs caused the cell cycle that had been arrested due to DNA damage by gamma rays to proceed conversely.
After 15 hours at 5 Gy gamma radiation
On the other hand, exposure to EMFs alone somewhat arrested the cell cycle.
This result suggests that EMFs have the effect of attenuating cell cycle checkpoints.

