Replication Stress

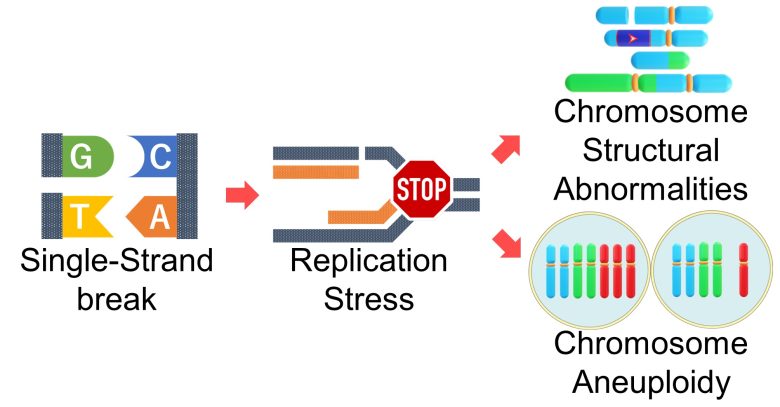
Replication stress caused by single-strand breaks leads to further large-scale mutations, chromosome structural abnormalities and aneuploidy.
I will explain how it works, mainly based on a 2015 France review article about replication stress. (Gelot et al. 2015)
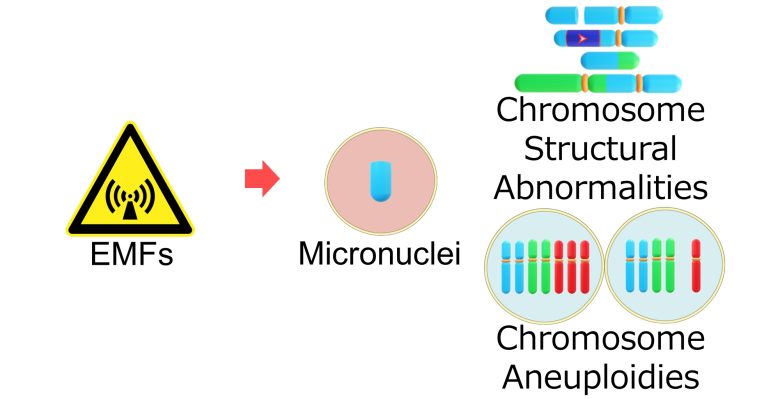
I will then present studies showing that EMFs did indeed cause the various types of mutations I have explained up to this point.
A study showed that 9 hours of exposure to cell phone EMFs and 20 minutes of exposure to radioactivity caused about the same level of chromosome abnormalities, telling us how harmful EMFs can be.
Table of ContentsAll_Pages
Chromosome Structural Abnormalities
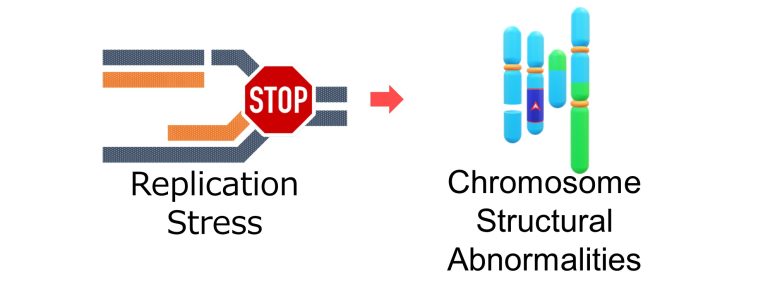
First, I will explain how replication stress can cause chromosome structural abnormalities.
Formation of Double-Strand Breaks
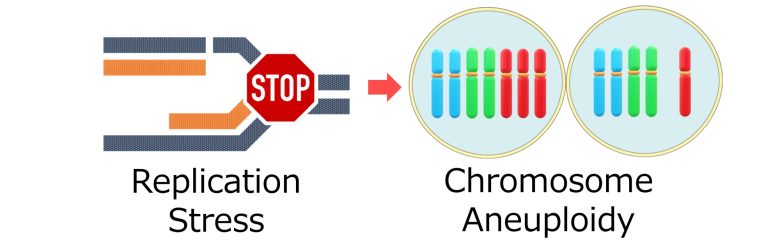
When a single-strand break is encountered during DNA replication, DNA replication stops there and replication stress occurs.
The major problem here is that the single-strand break in the original DNA forms a double-strand break with the new DNA. (Gelot et al. 2015)
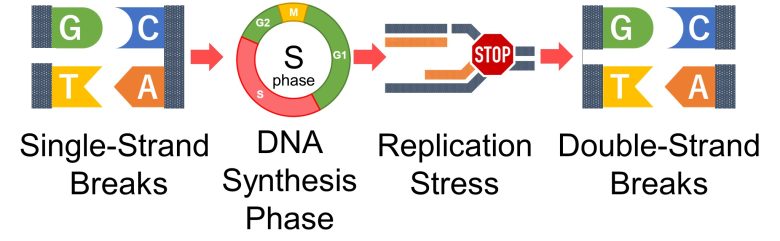
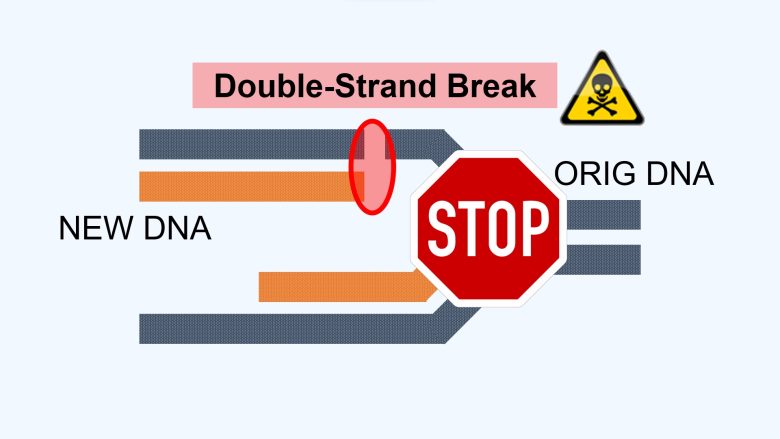
So, an increase in ROS causes an increase in DNA single-strand breaks, which directly leads to an increase in double-strand breaks during DNA synthesis.
Therefore, it follows that there will be an increase in repair errors of double-strand breaks, resulting in an increase in chromosome structural abnormalities such as chromosome deletions, inversions, translocations, and acentric and dicentric chromosomes.
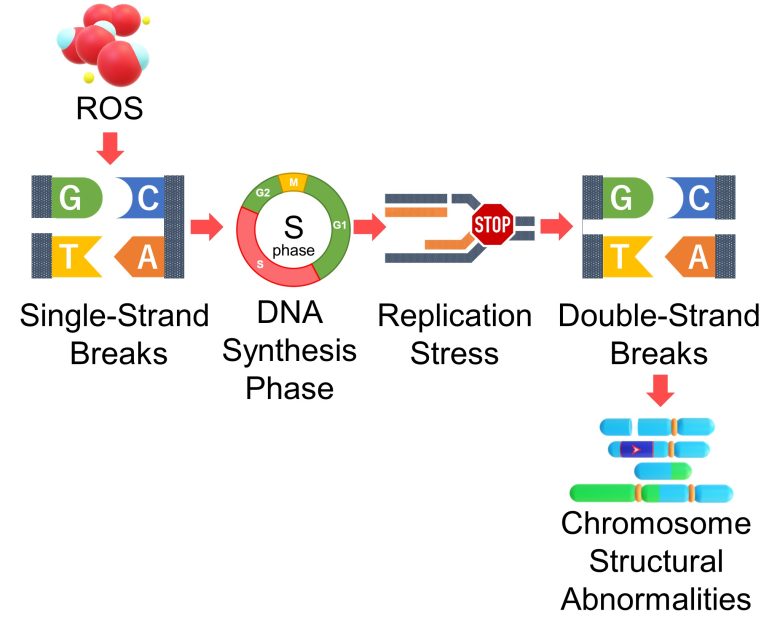
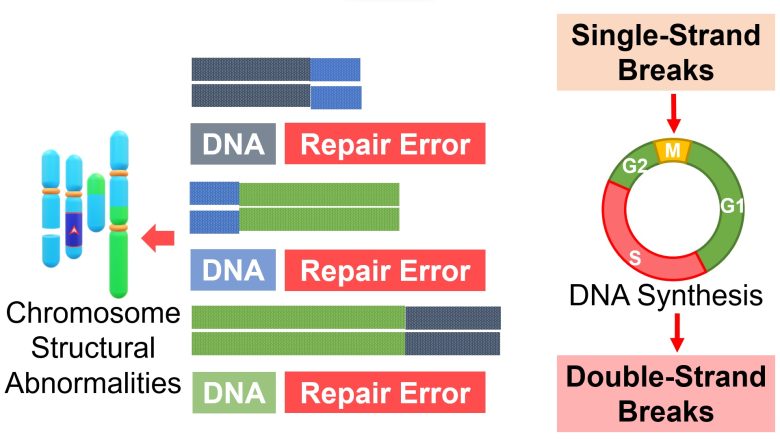
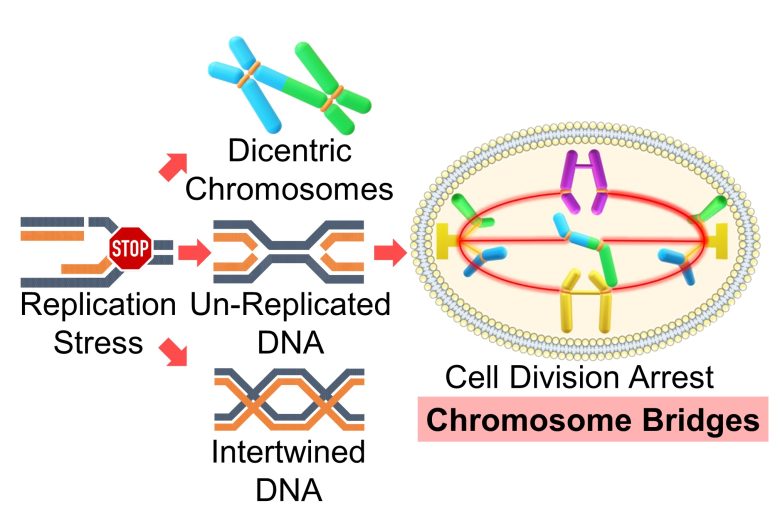
Formation of Chromosome Bridges
Replication stress converts single-strand breaks into double-strand breaks, and repair errors of double-strand breaks result in various chromosomal structural abnormalities.
Among these, dicentric chromosomes, which have two centromeres, form chromosome bridges and arrest cell division.
In addition to this, due to replication stress, DNA remains un-replicated or replicated DNA becomes intertwined, which also forms chromosome bridges. (Gelot et al. 2015)
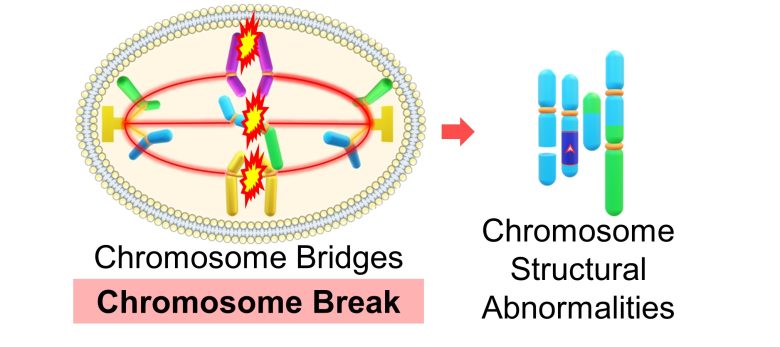
These chromosome bridges are resolved by chromosome breaks, which exacerbate chromosome structural abnormalities. (Gelot et al. 2015)
Chromosome Aneuploidy
Next, I will explain how replication stress can cause chromosome aneuploidy
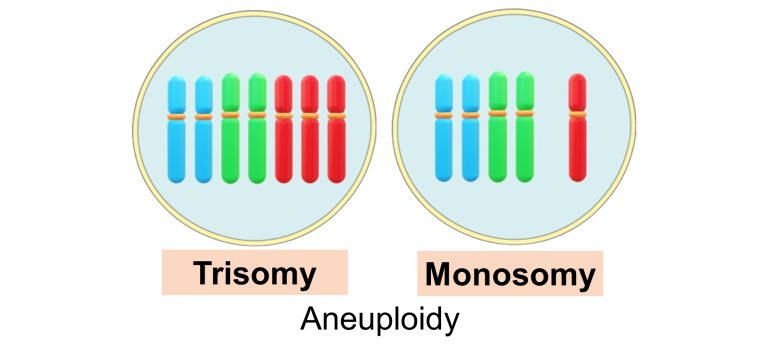
What is Chromosome Aneuploidy?
Human chromosomes are composed of pairs of two chromosomes, one each inherited from the father and mother, for a total of 23 pairs, or 46 chromosomes. One of the pairs is an X and Y sex chromosome that determines sex.

And chromosomal aneuploidy refers to having more or fewer of these chromosomes.
In particular, an increase in the number of chromosomes from a pair (= two) to three is called trisomy, while a decrease to one is called monosomy.
Aneuploidy from Replication Stress
Based on a 2019 Swiss paper, here is a pathway of chromosome aneuploidy caused by replication stress. (Wilhelm et al. 2019)
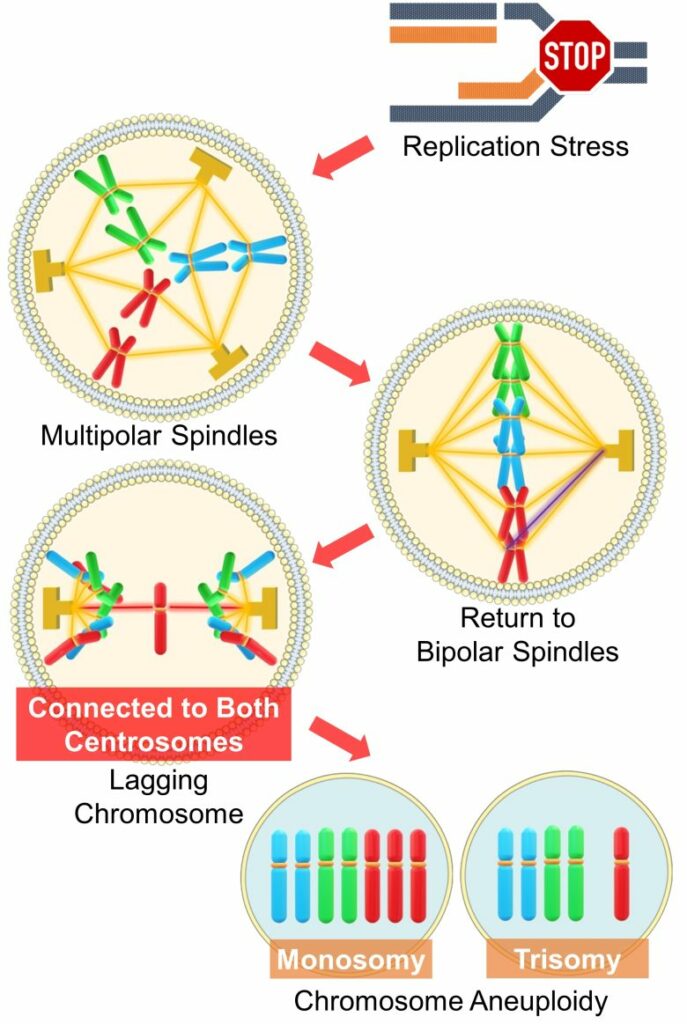
Aneuploidy from Replication Stress
( Cited and Modified from Wilhelm et al. 2019 )
- Extra centrosomes emerges due to replication stress, forming multipolar spindles (three or more centrosomes).
- Multipolar spindles are usually returned to bipolar spindles.
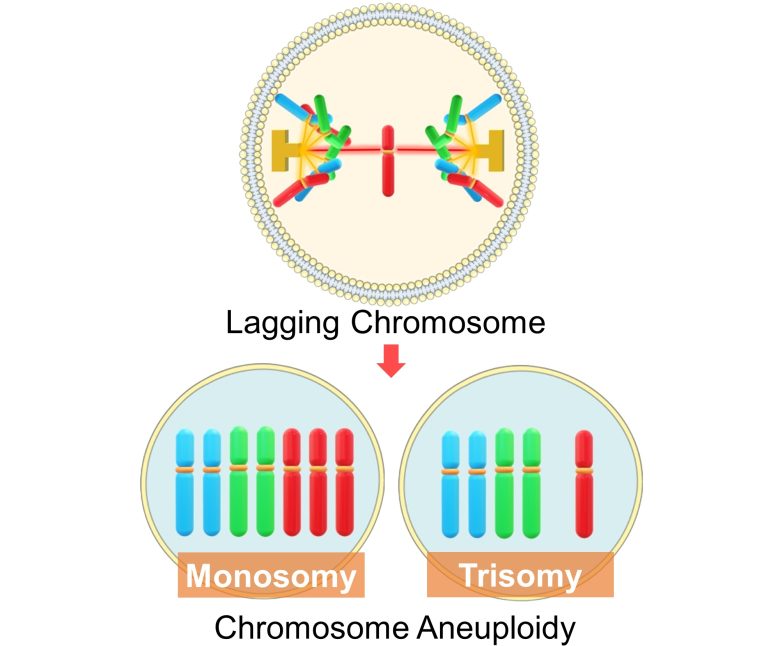
- However, in the process of correction, chromosomes that have become connected to both spindle poles, called lagging chromosomes, emerge.
- Incorrect distribution of a lagging chromosome causes the chromosomes that should be separate to belong to the same cell nucleus.
- This results in chromosome aneuploidy, where one cell has one more chromosome (trisomy) and the other has one less (monosomy).
Lagging chromosomes may also form micronuclei without being able to belong to either cell nucleus. This also causes chromosomal aneuploidy, especially monosomy. (Norppa 2003)
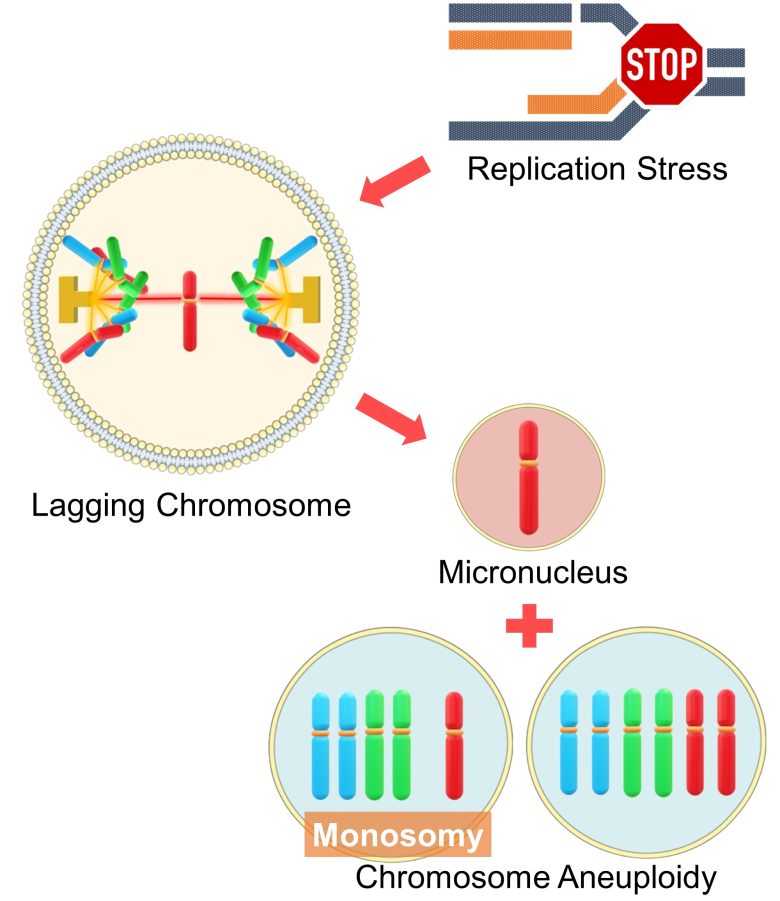
In mammalian cells, chromosomes connected to both spindle poles, or lagging chromosomes, are a major mechanism of aneuploidy. (Cimini et al. 2001)
Recap of Replication Stress
Below is a recap of the pathways from replication stress to chromosome abnormalities.
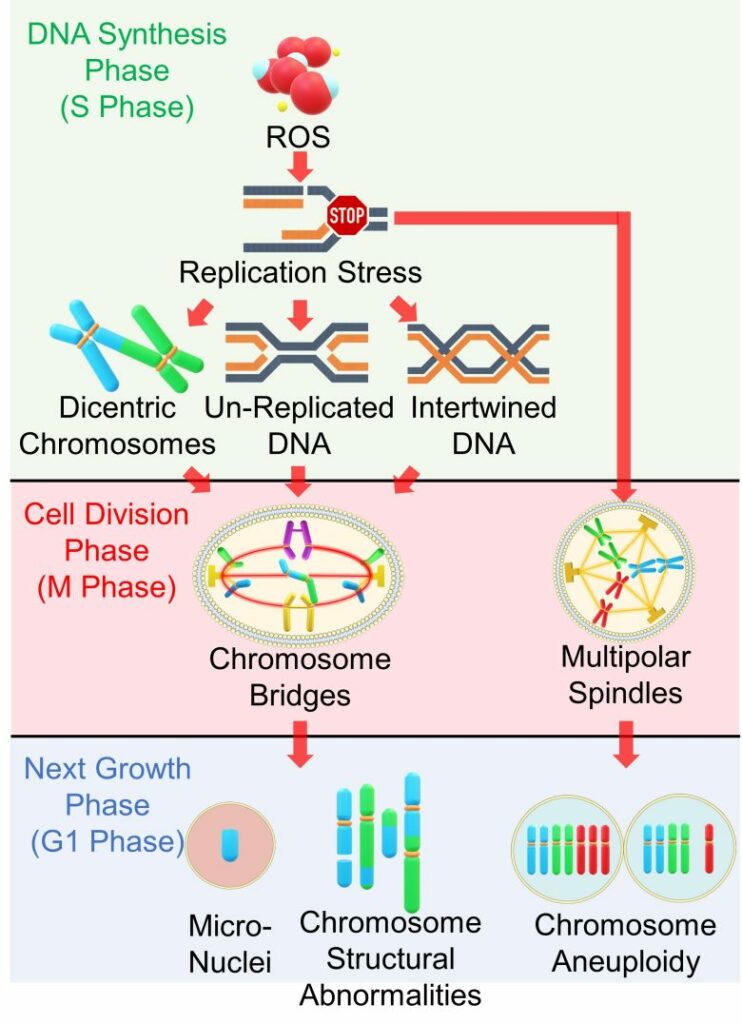
Chromosome Abnormalities from Replication Stress
( Cited and Modifiied from Gelot et al. 2015 )
- Replication stress occurs during the DNA synthesis phase due to factors such as ROS.
- Replication stress causes chromosome structural abnormalities such as dicentric chromosomes.
- It also leaves DNA unreplicated and also intertwines replicated DNA.
- When these abnormalities reach cell division phase, cell division is arrested and chromosome bridges are formed.
- The chromosomal bridges are resolved by chromosome breaks, exacerbating the chromosomal structural abnormalities.
- Replication stress also causes the formation of multipolar spindles.
- The multipolar spindles lead to incorrect distribution of chromosomes, resulting in chromosome aneuploidy.
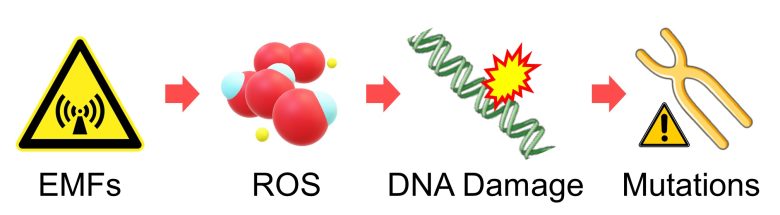
Recap of Mutation
The pathways of mutations from DNA damage, including replication stress, up to this point is summarized in the figure below.
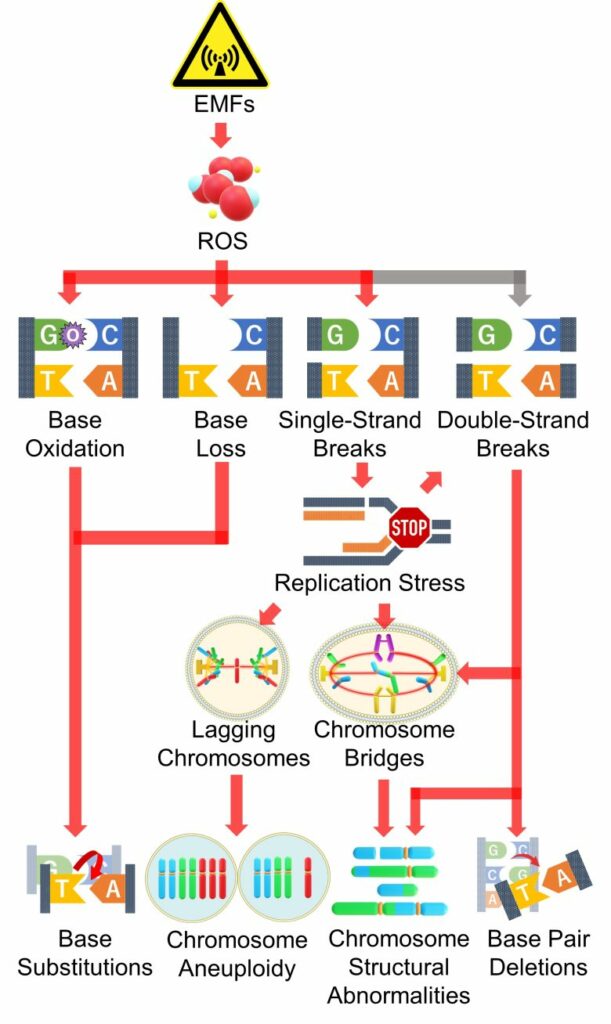
Mutations by EMFs
Here, I will present studies showing that mutations occurred with EMF exposure.
Studies
Pesnya and Romanovsky 2013
Cell phones with a local SAR of 1.4 W/kg were placed and kept in talk mode for 1 or 3 hours per day, and freshly sprouted onion bulbs were exposed to their EMFs at a distance of 0.6 inch (1.5 cm) for 3 days.
As a result, chromosome bridges, lagging chromosomes, chromosome stickiness, chromosome fragments, and micronuclei increased as exposure time increased.
Compared to a group exposed to radioactivity (plutonium-239 alpha particles), the damage caused by the 9 hours (3 hours per day x 3 days) of cell phone EMF exposure was comparable to that of the 20 minutes of radioactivity exposure.
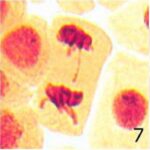
Normal Cell Division

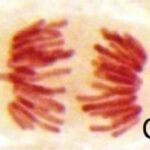
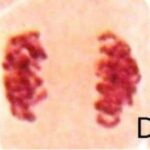
Normal cell division was observed in the control group.
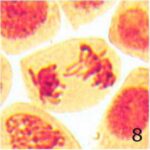
Increase in Chromosome Bridges 1
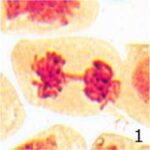
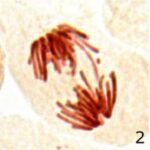
Due to 9 hours of cell phone EMF exposure, chromosome bridges increased.
Increase in Chromosome Bridges 2
The frequency of chromosome bridges increased 9-fold due to 9 hours of cell phone EMF exposure and 4-fold due to 20 minutes of radioactivity exposure.
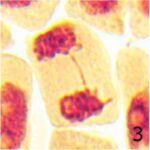
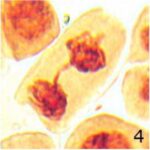
Increase in Lagging Chromosomes 1
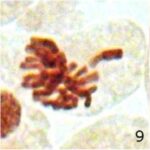
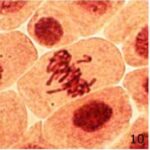
Due to 9 hours of cell phone EMF exposure, lagging chromosomes increased.
Increase in Lagging Chromosomes 2
The frequency of lagging chromosomes increased 18-fold due to 9 hours of cell phone EMF exposure and 3-fold due to 20 minutes of radioactivity exposure.
Increase in Chromosome Stickiness 1
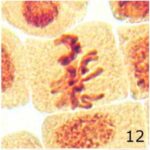
Due to 9 hours of cell phone EMF exposure, chromosome stickiness increased.
Increase in Chromosome Stickiness 2
The frequency of chromosome stickiness increased 20-fold due to 9 hours of cell phone EMF exposure and 13-fold due to 20 minutes of radioactivity exposure.
Increase in Chromosome Fragments 1
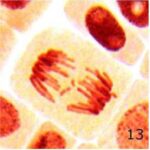
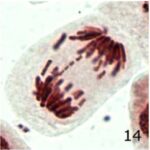
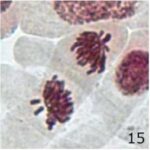
Due to 9 hours of cell phone EMF exposure, chromosome fragments increased.
Increase in Chromosome Fragments 2
The frequency of chromosome fragments increased 5-fold due to 9 hours of cell phone EMF exposure and 16-fold due to 20 minutes of radioactivity exposure.
Increase in Micronuclei 1
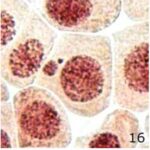
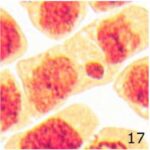
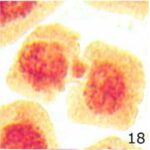
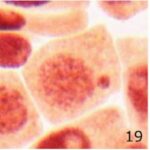
Due to 9 hours of cell phone EMF exposure, micronuclei increased.
Increase in Micronuclei 2
The frequency of micronuclei increased 14-fold due to 9 hours of cell phone EMF exposure and 23-fold due to 20 minutes of radioactivity exposure.
Other Abnormalities
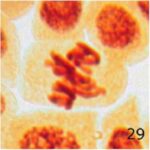
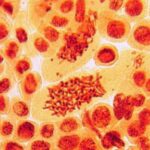
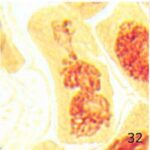
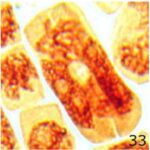
Due to 9 hours of cell phone EMF exposure, multipolar cell division, giant polyploid cells, and unspecified abnormalities occurred.
D’Ambroslo et al. 1985
Blood was taken from cattle and blood lymphocytes were exposed to 50 Hz ELF-EMFs with a strength of 16 mV/m for 72 hours.
As a result, chromosome breaks, structural abnormalities, aneuploidy, fragments, and polyploidy increased.
Increase in Chromosome Breaks
The percentage of chromosome breaks increased 3-fold due to the EMF exposure.
Increase in Structural Abnormalities
The percentage of chromosome structural abnormalities increased 10-fold due to the EMF exposure.
Increase in Aneuploidy
The percentage of chromosome aneuploidy increased 3-fold due to the EMF exposure.
Increase in Fragments
The percentage of chromosome fragments increased 2-fold due to the EMF exposure.
Increase in Polyploidy
The percentage of chromosome polyploidy increased 5-fold due to the EMF exposure.
Zothansiama et al. 2017
For study participants in Aizawl city, Mizoram, India, ROS in blood increased and micronuclei in blood lymphocytes increased as the distance from homes to cell towers decreased.
The strength of RF-EMFs averaged 0.0035 μW/cm2 outside 300 m of the cell towers and 0.5 μW/cm2 within 80 m.
Increase in ROS
An increase in lipid peroxidation and a decrease in antioxidant activity mean an increase in ROS.
Increase in Micronuclei
The frequency of micronuclei increased by 70% within 20 m of the cell towers.
Mairs et al. 2007
Human glioma cells were exposed to 50 Hz ELF-EMFs with a strength of 1 mT for 12 hours.
As a result, DNA mutation increased. The major mutations were loss of heterozygosity and allelic imbalance, both of which represent an increase in loss of single genes.
Also, ionizing radiation-induced mutations were amplified when 0.3 or 3 Gy of ionizing radiation was combined with ELF-EMFs. (*)
One possible cause is that EMFs attenuate cell cycle checkpoints (see page 6).
Increase in Mutation
Othman et al. 2001
For male air traffic controllers and engineers in Egypt, as well as randomly chosen males, aneuploidy of chromosomes 7, 17, and Y chromosome in blood lymphocytes increased when they were occupationally exposed to EMFs from radar screens, antennas, satellite installations, and closed circuit televisions (CCTVs).
Increase in Aneuploidy
The percentage of aneuploidy (monosomy, loss) increased 6-fold for chromosome 7, 4-fold for chromosome 17, and 4-fold for Y chromosome due to the occupational exposure to EMFs from the radar screens, antennas, satellite installations, and CCTVs.
Mashevich et al. 2003
Blood was taken from male Israeli study participants and blood lymphocytes were exposed to 830 MHz RF-EMFs at a culture-medium average SAR of 2-8.2 W/kg for 72 hours.
As a result, for chromosome 17, abnormal DNA replication and aneuploidy increased as the SAR value increased.
Increase in Abnormal DNA Replication
For chromosome 17, the percentage of abnormal DNA replication increased as the SAR value increased.
Increase in Aneuploidy
For chromosome 17, the percentage of aneuploidy increased as the SAR value increased.
Manikowska-Czerska et al. 1985
Mice 8-10 weeks old, equivalent to adolescents, were exposed to 2.45 GHz RF-EMFs at a whole-body average SAR of 0.05-20 mW/kg for 30 minutes per day for 2 weeks.
As a result, in spermatogenic cells (sperm-producing cells) within the testes, translocations, which are chromosome structural abnormalities, and univalent chromosomes increased.
Univalent chromosomes are chromosomes that are not paired during cell division and, like lagging chromosomes, cause aneuploidy. (Nagaoka et al. 2012)
Increase in Translocations
The percentage of translocations increased due to the RF-EMF exposure.
Increase in Univalent Chomosomes
The percentage of univalent chromosomes increased due to the RF-EMF exposure.
It is noteworthy that the EMFs of the same frequency as Wi-Fi showed biological effects even at the weak strength of 0.00005 W/kg, the whole-body average SAR.
Balamuralikrishnan et al. 2012
For study participants in Coimbatore city, Tamil Nadu, India, chromosome breaks and micronuclei in blood lymphocytes increased when they worked inside/near high-voltage substations.
Increase in Chromosome Breaks
The frequency of chromosome breaks increased 2-fold with the work near the high-voltage substations and 3-fold with the work inside.
Increase in Micronuclei
The frequency of micronuclei increased 3-fold with the work near the high-voltage substations and 3-fold with the work inside.
That's all for the presentation of the studies.
We have confirmed that EMFs can indeed cause mutations such as micronuclei, chromosome structural abnormalities, and aneuploidy.